Product User - Experience Elements
2024-11-29 09:48:25 118 0 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
Other creations by the author
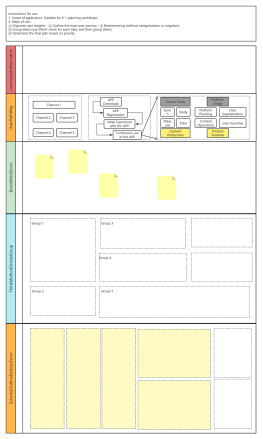
Outline/Content
01 The definition of user experience
Definition: User experience is not about how a product functions, but how users interact with and use it.
Product Design
Function Design
Exterior Design
User Experience Design
The more complex a product is, the more difficult it is to provide a good user experience.
Product features and properties are important, while user experience has a greater impact on customer loyalty.
A major criterion for measuring user experience is: conversion rate.
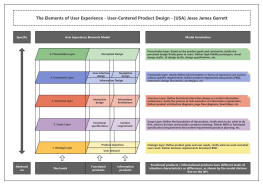
02 Five Elements of User Experience
Presentation Layer: The final effect of the page displayed to the user
The framework layer: how the page is designed and laid out
Structure Layer: The framework is the concrete expression of the structure, and the structure layer determines where users come from and where they go.
Scope layer: What functions and features the product provides for users
Strategic level: What can users get, what can we get
duplicity
Functional products
Information Products
03 Strategic Layer
Product Objective
Business objective
Success Indicator
Brand Identity
User needs
User segmentation
Demographic characteristics
Consumption mentality
Understanding and adapting to technology
The level of professional understanding of relevant content
The user of information
Usability and User Research
Qualitative analysis
User Interview
Focus group
Usability Test
Quantitative analysis
Questionnaire survey
A/B testing
User portrait
04 Scope Layer
The meaning of scope layer
I know what you want to do
Knowing what you don't want to do
Category
Functional products
Information Products
Confirm the priority of requirements
05 Structural Layer
Interaction Design
Possible user behaviors
How the system cooperates and responds
Error handling
Information Architecture
Create a classification system
From top to bottom
from bottom to top
Structural approach
Node: Corresponding to any information fragment or combination
It can be as small as a page element or as large as the entire website
It can be as small as a page element or as large as the entire website
Structural Classification
Tree structure
Matrix structure
Natural structure
Linear structure
Organizational Principle: Nodes are placed in the information architecture based on the organizational principle.
Language and metadata
Controlled vocabulary
Classifier Dictionary
Metadata: Information about information
06 Framework Layer
Interface design: Provide users with the ability to do something
Select the correct interface element
Help users complete their tasks
Make this process easy to understand and use through appropriate means.
Navigation design: Provide users with the ability to go somewhere
Provide a method for users to jump between websites.
Convey the relationship between these elements and the content they contain.
It must convey the relationship between its content and the current page the user is browsing.
Information Design: Conveying Ideas to Users
Visual presentation of information
Classification or organization of information
Habit and metaphor
07 Presentation Layer
Perceptual Design
Vision
Provide support for the product.
The user's eye movement follows a smooth path.
No need for too many details, provide effective guidance for users.
Design Principles
contrast
Consistency
auditory
Widely used
tactile
Industrial Design
Vibration
Olfaction and taste
08 The application of element
Methodology
Understand the problem you are trying to solve
Understand the consequences of these solutions
General status
Design determined by the status quo
Design determined by imitation
Design determined by the leader
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More