Consumer Psychology
2024-09-26 10:56:31 155 0 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
This mind map delves into the intricacies of consumer psychology, exploring key concepts such as mental accounting, sunk cost, proportion bias, loss aversion, and price anchoring. Mental accounting reveals how consumers categorize money into different psychological accounts, affecting purchasing decisions. The sunk cost fallacy highlights how past investments influence future choices, while proportion bias demonstrates consumers' sensitivity to relative price changes. Loss aversion explains the greater impact of losses over gains on consumer behavior. Finally, price anchoring shows how consumers evaluate product prices through comparison. Understanding these principles can transform marketing strategies and consumer interactions.
Other creations by the author
Outline/Content
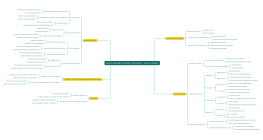
Mental accounting
concept
Money is categorized and stored in different psychological accounts, although they are in the same room but independent of each other.
case
Before the concert, losing 200 yuan => If it's a 200 yuan bus card, most people choose to continue watching
apply
Hundreds of dollars of chocolate placed in the emotional maintenance account during promotion will have a higher purchase rate compared to the living expenses account.
The renovation plan of the decoration company helps customers save several square meters of space => Save money in the house purchase account instead of spending more in the renovation account.
Summary
Change the customer's perception of your product, so that they shift from the mental account where they don't want to spend money to the one where they are willing to pay for it.
Sunk cost
concept
Deciding to do something => Not only looking at the benefits of this thing in the future, but also paying attention to whether you have invested in it in the past.
case
The governments of the UK and the US jointly invested in the development of a large supersonic passenger plane, but although it was successfully developed, the two governments suffered huge losses.
apply
Haggling over clothes => Customers repeatedly try on and select, staff spend a lot of energy, in order not to lose the sunk cost may give more preferential
Asking customers to pay a deposit may cause them to lose their desire to buy when they return home, but they will still purchase your product to avoid losing the deposit.
Hosting a grand wedding -> invested a lot of manpower and financial resources, if you get into a fight and want to break up, you feel that it's too troublesome to hold another one, so you choose to compromise.
Summary
Sunk costs have no good or bad, but they are stubborn. You can deliberately create sunk costs for the other party to increase the success rate of the transaction.
For us, if we can overcome the bias brought by sunk costs, we may make more rational business judgments.
The proportion bias
concept
People are more sensitive to the perception of proportions than to the perception of numerical values themselves.
case
The same alarm clock, if A store 100 yuan, B store 60 yuan => many people will spend 10 minutes from A to B to save 40 yuan
The same luxury watch, if C store is 6600 yuan, D store is 6550 yuan => Many people tend to give up 10 minutes and still buy at C store.
apply
Compared with a 1,000 yuan pot with a 50 yuan spoon, a 1 yuan upgraded version of the 50 yuan spoon is more likely to impress consumers.
The purchase rate of 200 yuan 4G memory sticks is very low for customers -> 4G memory computers cost 4800 yuan while 8G memory computers only cost 5000 yuan.
Summary
Using the exchange method to attract consumers' attention to small items with a large price change ratio will make them feel like they are getting a great deal.
Selling cheap accessories together with an expensive item can make consumers feel more value than selling them separately.
Loss aversion
concept
Getting happiness doesn't actually relieve the pain of loss.
case
The old man drives the children playing on the public lawn away, first giving 10 yuan, then 5 yuan and finally 1 yuan => Although the child can get 1 yuan, the pain of losing 9 yuan is far greater than the joy of getting 10 yuan.
apply
The furniture mall charges a 20 yuan delivery fee, which may trigger the loss aversion mentality of consumers -> If you don't need delivery, you can save 20 yuan.
Consumers worry about what to do if the furniture is broken when buying it -> Provide a 7-day return and exchange policy without reason.
Consumers love to buy your sofa, but they already have one at home. -> Trade-in for a new one, with XX yuan discount for the old sofa, which is more tempting for customers.
Summary
The way of exchanging (trading in old for new) is more attractive to customers than the way of discounts.
Replace the lost expression framework with the acquired one.
Price Anchor
concept
Consumers will use two principles to judge whether the product price is appropriate when they are not sure about the price -> avoid extremes and weigh against each other.
case
When staying at a hotel for a business trip, choosing the online payment plan => 80 yuan per hour and 105 yuan for the whole day, most people choose the latter, because 105 yuan is a good deal, while 80 yuan is the price anchor.
apply
Two water purifiers, 1399 yuan and 2288 yuan => Everyone will buy the 1399 one, while the 2288 wants to increase sales, it's best to have another 4399 one.
A 600 yuan physical examination product => If you compare it from the side, spending 6000 yuan to maintain a car but not willing to spend 600 to maintain yourself may be more effective.
Summary
The principle of guiding purchases: avoid extremes -> When there are three or more choices, most people tend to choose the middle one.
The second principle of guiding purchases: weighing and comparing -> When customers have no way to judge the value, they will choose a product they think is similar to compare, so that they have a standard to measure by.
Consumers don't pay for the cost of goods, but for the perceived value of the goods. The logic of price anchoring is to give consumers a comparable price perception.
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More