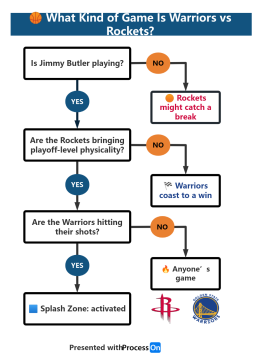
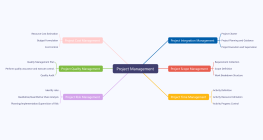
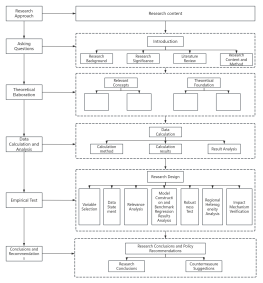
Core Control Points of Project Management
2024-10-14 18:47:46 165 1 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
This mind map outlines the 'Core Control Points of Project Management,' highlighting essential aspects for successful project execution. It emphasizes goal orientation through SMART principles, ensuring clear scope definition to prevent scope creep, and meticulous time planning with progress monitoring. Resource allocation is optimized by identifying and prioritizing needs, while risk prevention strategies are developed to mitigate potential setbacks. Quality control and cost management are maintained through standards and budgeting. Effective communication, stakeholder interest coordination, and teamwork are prioritized, along with flexibility in response to changes. Contract performance, progress tracking, outcome assessment, and project summary ensure comprehensive project management.
Other creations by the author
Outline/Content
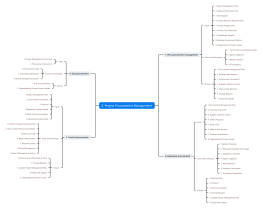
Interest coordination
Identify interests: Understand the needs and expectations of all stakeholders.
Balancing interests: Finding a balance point between meeting the needs of different stakeholders.
Interest management: Respond promptly to the feedback and changing needs of stakeholders.
Teamwork
Team building: Establish a team with common goals and good collaboration.
Role assignment: Clarify the roles and responsibilities of each team member.
Team motivation: Improve team morale and motivation through incentive measures.
Be flexible in response
Change Management: Establish an effective change management process to deal with changes in the project.
Quick response: Make decisions and adjustments quickly when changes occur.
Adaptive planning: Develop a project plan that can be flexibly adjusted.
contract performance
Contract Understanding: Ensure that the team understands all the terms and conditions of the contract.
Contract monitoring: follow up on the implementation of contracts to ensure compliance.
Contract issue resolution: promptly resolve any issues that arise during the contract execution process.
Progress Tracking
Progress Report: Generate progress reports regularly to understand the project status.
Progress Comparison: Compare the actual progress with the planned progress to identify deviations.
Adjust the progress: Adjust the project plan as needed to adapt to the actual situation.
Outcome assessment
Outcome Check: Regularly inspect the outcomes of cultivation projects to ensure they meet expectations.
Outcome feedback: Collect user and stakeholder feedback, assess the acceptance of the outcomes.
Improve the results: Make necessary improvements based on the feedback.
Project Summary
Experience Record: Record the lessons and experiences learned during the project process.
Knowledge Sharing: Share lessons learned with teams and organizations to promote knowledge accumulation.
Future Planning: Based on the lessons learned, make better plans for future projects.
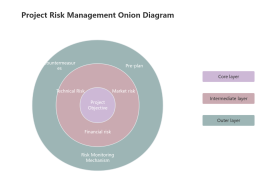
Goal-oriented
Clarify the goal: Know what specific goals the project aims to achieve.
SMART Principle: Ensure goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Objective sharing: Ensure that the team and all stakeholders understand and agree on the project objectives.
Scope definition
Define clear boundaries: clearly define the scope of the project, know what must be completed and what is not.
Avoid scope creep: Prevent the project scope from expanding unlimitedly, resulting in resource waste.
Scope confirmation: Ensure that all key stakeholders have a consensus on the project scope.
Time planning
Create a plan: Develop a detailed timeline, including all key milestones and deadlines.
Allocate time reasonably: Allocate enough time for each task to avoid being too tense or dragging.
Monitor progress: Check project progress regularly to ensure that the project is progressing as planned.
Resource Allocation
Resource Identification: Understand what resources the project requires, including human, material, and financial resources.
Priority sorting: Allocate resources based on the importance and urgency of tasks.
Resource optimization: Ensure maximum efficiency in resource usage and avoid waste.
Risk prevention
Risk Identification: Identify potential risks that may affect the project in advance.
Risk Assessment: Assess the probability and impact of each risk.
Risk Response: Develop a response strategy for each risk to minimize its negative impact on the project.
Quality control
Quality standards: Set the quality standards and acceptance criteria for the project.
Quality Monitoring: Continuously monitor quality throughout the project process to ensure compliance with standards.
Quality Improvement: Improve the quality based on feedback, enhance the project results.
Cost control
Cost budget: Develop a detailed cost budget, including all expected expenses.
Cost tracking: Monitor actual expenses and compare them with the budget.
Cost optimization: Find ways to reduce costs without compromising project quality.
Communication is smooth.
Communication Plan: Develop a communication strategy and clarify what information needs to be known.
Information Sharing: Ensure timely sharing of information among team members and stakeholders.
Communication Methods: Choose appropriate communication tools and methods to improve communication efficiency.
Collect
Collect
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More