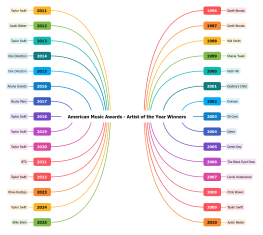
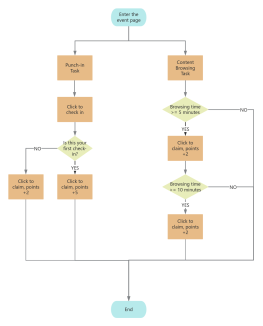
Factory business bracket diagram
2024-11-12 11:03:04 128 0 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
The 'Factory Business Bracket Diagram' mind map provides a comprehensive overview of factory operations with a focus on profitability. It outlines key areas such as main business income from various product lines, including HR, lubricant, OPE, and UCP products. The mind map delves into cost structures, emphasizing the importance of standard and actual cost management. It explores strategies for maintaining and increasing profitability through markup rates, production capacity management, and strategic pricing. Additionally, it highlights the impact of four major expenses—sales, administrative, financial, and R&D—on net profit, while also considering cash flow, inventory management, and continuous cost reduction strategies.
Other creations by the author
Outline/Content
Main Business Income
HR products
Lubricant products
OPE products
UCP Product
Main business cost (standard cost + actual cost difference)
Standard Cost
Step cost: Achieve step cost price according to the amount
Standard cost ensures accuracy
Working Hours: The working hours for products in the same series are the same, and the differences are in different configurations.
Purchased price: guaranteed accurate and reasonable
BOM changes are promptly transferred to cost, and the standard cost is changed simultaneously.
Actual cost variance
Quantity difference
Fee difference
Price difference
Main business profit
Gross profit from main business = Main business revenue - Actual cost
Gross profit from main business = Quoted profit + Actual cost difference
Gross profit from main business = Quoted profit + Actual cost difference
Actual cost = standard cost + actual cost variance = actual material input (BOM feeding) + manufacturing cost input + material price variance
Quotation Profit
The markup rate determined by different product lines
Premium rate
The company determines the initial markup rate.
When production capacity is insufficient
The number of orders received in the current month exceeds the break-even production volume.
High-profit products are priced according to the company's determined markup rate.
Products with low profit margins can increase their profitability by raising their markup.
The monthly order intake is below the break-even production volume.
Offering discounts to attract more orders and increase revenue and sales.
Increase production capacity
When production capacity is sufficient
The number of orders received that month exceeds the break-even production volume.
Open source: Offering discounts to attract more orders and sales, reducing the markup rate.
Throttling: If orders cannot be obtained, reduce expenses and reduce variable costs.
The order volume for the month is below the break-even production capacity.
Open Source: Discount Promotion, Increase Rate Reduction
Throttling: If unable to obtain orders, reduce expenses, reduce fixed costs
Profit contribution point product
Celebrity products
High-profit products
High-selling products - positioning strategy focuses on cost reduction
High-profit products - positioning strategy appropriately reduces the markup rate to obtain more volume
Loss-making products
Products with strategic loss of meaning
The retention - positioning strategy is to achieve no loss or minimal loss
High-cost products or non-competitive products
The selling price is competitive: raise the selling price for products in demand, and take off the shelves for products without demand.
Price is not competitive: off the shelf
Four expenses
Sales Expenses - After-sales Expenses
Cost of quality loss due to post-sales parts or product costs
After-sales service fee
Return shipping fee
Administrative Expenses
Non-production unit expenses
Financial expenses
Capital Occupation Fee
Settlement, etc.
R&D expenses
According to the actual occurrence of the project
Other Operating Revenue
The net profit of the factory = the main business profit - the four expenses + the income from other businesses
Cash flow
Accounts Payable
Billing period
Payment Method
Accounts Receivable
Billing period
Payment Method
inventory
raw materials
Work in progress
Finished products
Continuous cost reduction
Continuous optimization of product structure
The continuous upgrading of the working method
The continuous improvement of team capabilities
Continuous optimization of the supply chain
Create hot products + star products
Based on market demand and positioning, we promote products at the most competitive price while ensuring quality, and achieve final revenue through volume.
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More