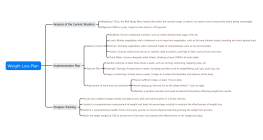
Loss aversion: Consumers are more afraid of losing.
2024-09-26 10:56:31 140 0 Report 0
1
Login to view full content
This mind map explores the concept of 'Loss Aversion: Consumers are more afraid of losing,' a psychological and economic principle highlighting individuals' tendency to prefer avoiding losses over acquiring equivalent gains. It delves into the psychological foundations, such as the Loss Aversion Theory and Mental Accounting Theory, and examines how these principles manifest in consumer decision-making. The mind map also addresses marketing strategies that leverage loss aversion, emphasizing returns and creating urgency. Additionally, it considers individual differences, such as age, gender, and cultural background, which influence loss aversion and consumer behavior.
Other creations by the author
Outline/Content
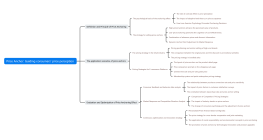
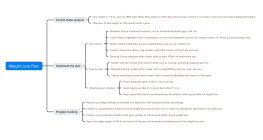
The definition and principles of loss aversion
Psychological Foundation: Loss Aversion Theory
The perceived difference between loss and gain
Mental Accounting Theory
Asymmetric preference
Economic Perspective: Risk Aversion Behavior
Loss aversion in prospect theory
Deterministic effect
Probability-weighted bias
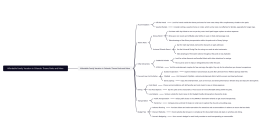
The manifestation of loss aversion in consumer decision-making
Conservative tendencies in purchase decisions
Avoid high-risk options
Insurance product preference
The attraction of discounts and preferential policies
Unwillingness to let go in decision-making
Sunk Cost Fallacy
Sticking to failed investments
The influence of sentimental attachment to old things
Loss Perception in Comparison Shopping
Relative price and reference price
Anchoring effect
Price Sensitivity
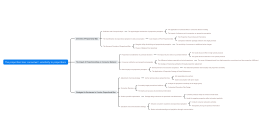
Application of Loss Aversion Marketing Strategy
Avoid mentioning losses directly.
Emphasize returns and added value
Promotion of Value-added Services
The presentation of return on investment
Promote using the psychology of loss aversion
Limited-time offer and urgency creation
Countdown Promotion
Limited edition products on sale
Build security assurance and return policy
No reason return and exchange policy
Enhance consumer trust
Reduce the regret after purchase
Social Identity and Group Effect
Herd mentality and word-of-mouth marketing
User Evaluation and Recommendation System
Leveraging social media influence
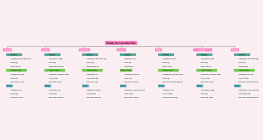
Individual Differences and Influencing Factors of Loss Aversion
Age and gender differences
The impact of age on risk tolerance
The consumption habits of young and old
The Role of Gender in Consumer Decision Making
Cultural background and values
Loss Aversion under Eastern and Western Cultural Differences
Collectivism and individualism
Consumer Views of Different Religious Beliefs
Financial situation and mental accounting
Income level and consumption decision
The consumption pattern of the affluent class
Conservative choice under economic pressure
Emotional state and cognitive bias
The impact of emotions on the decision-making process
Positive emotions and impulse buying
Negative emotions and risk aversion
Collect
Collect
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More