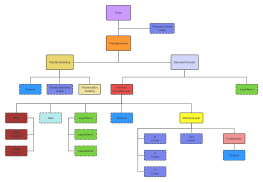
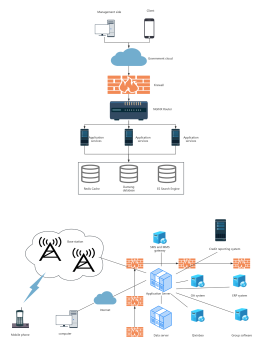
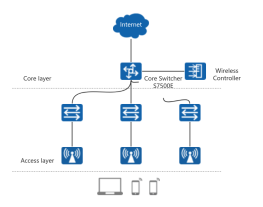
Network Topology Diagram Structure
2024-09-14 11:53:17 202 1 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
The mind map titled 'Network Topology Diagram Structure' provides an insightful overview of various network topologies, essential for understanding network design and functionality. It covers star, ring, bus, tree, mesh, mixed, cellular, and distributed topologies, highlighting their unique structures, advantages, and disadvantages. Each topology is analyzed for its applicability in different network scenarios, such as LANs, wireless networks, and large enterprise networks. The map also discusses the implications of topology choices on network reliability, scalability, and maintenance complexity, offering a comprehensive guide for network engineers and IT professionals.
Other creations by the author
Outline/Content
Star topology
Introduction
A star topology refers to a network where workstations are connected in a star pattern, in which each node is connected to a central node (usually a switch or hub) via point-to-point links. The central node is responsible for managing network traffic, and if the central node fails, all nodes connected to it will lose connectivity.
Advantages
Easy to install and troubleshoot, the failure of any single node will not affect the communication of other nodes.
Disadvantages
The central node becomes a single point of failure. If there is a problem with the central node, the entire network may be paralyzed.
Ring network topology
Introduction
Ring topology is commonly used in LANs. In this structure, the transmission medium extends from one end user to another, forming a ring that connects all end users. Data travels in one direction through the ring, passing from node to node. The most notable example is the token ring network.
Advantages
Simplified path selection, as data always flows along the loop.
Disadvantages
The failure of a single node or a link interruption can affect the communication of the entire loop,
and adding or removing nodes requires reconfiguring the loop.
and adding or removing nodes requires reconfiguring the loop.
Bus topology
Introduction
All nodes share a common transmission medium (bus), and data propagates along this linear link, with all nodes being able to monitor the data on the bus.
Advantages
Low cost, easy to expand, just connect the new nodes to the bus.
Disadvantages
The bus becomes a single point of failure, and as the number of nodes increases, performance degrades and the probability of conflicts rises.
Tree Topology Structure
Introduction
A tree structure is a hierarchical centralized network control system. Compared to a star structure, it has a shorter total length of communication lines and lower costs. Nodes are easy to expand, and finding paths is relatively convenient. However, except for leaf nodes and their connected lines, the failure of any node or its connected lines can affect the system. It is commonly used in large networks, such as campus or enterprise networks.
Advantages
For easy hierarchical management and fault isolation, with flexible expansion.
Disadvantages
Failures in the upper-level nodes can affect all subnets below them.
Mesh topology
Introduction
In a mesh topology, each device in the network has a point-to-point link connection with every other device. This type of connection is not cost-effective and is only used when each station needs to frequently send information. Its installation is complex, but the system reliability is high, with strong fault tolerance. It is one of the most reliable but also the most complex network structures. It is sometimes also referred to as a distributed structure.
Advantages
High reliability ensures that even if some links or nodes fail, data can still be transmitted through other paths.
Disadvantages
High costs, complex configuration and maintenance.
Mixed Topology Structure
Introduction
A network topology that combines a star or ring structure with a bus structure can better meet the needs of larger network expansion, solving the limitations of transmission distance in star networks, and also addressing the restrictions on the number of connected users in bus networks.
Advantages
Improve the reliability and availability of the network, with strong scalability and performance.
Disadvantages
High cost, complex design and configuration, difficult diagnosis and maintenance, may require special hardware and software.
Cellular topology structure
Introduction
This structure is commonly used in wireless networks, such as mobile phone networks, where the network is divided into multiple cells, each managed by a base station, which are interconnected through a backbone network. It is suitable for urban networks, campus networks, and enterprise networks.
Advantages
Efficiently manage radio spectrum to support a large number of mobile users.
Disadvantages
Requires complex frequency planning and inter-base station coordination.
Distributed Topology Structure
Introduction
Although not often listed as a fundamental network topology classification, it is becoming increasingly important in modern network design, especially in the fields of cloud computing and edge computing, where it emphasizes the distributed distribution of resources and services throughout the network.
Advantages
Enhance the overall resilience and processing capability of the system, and reduce dependence on centralized resources.
Disadvantages
The complexity of coordinating and managing distributed resources increases.
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More