Study Notes for Logic
2024-07-06 21:10:51 302 0 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
Discover comprehensive study notes on logic, covering essential topics such as the definition, importance, and applications of logic. Dive into propositional logic with insights on simple and compound propositions, logical connectives, truth tables, and logical equivalences. Explore predicate logic, including quantifiers, predicates, variables, and logical inference techniques like Modus Ponens and Modus Tollens. Learn about Boolean algebra, its functions, fundamental laws, and expression simplification methods. Understand the differences between deductive and inductive reasoning, and master formal proofs and logical fallacies. Get acquainted with set theory, including sets, subsets, and operations like union and intersection, as well as types of relations and functions. Delve into modal logic with modal operators, possible worlds semantics, and modal axioms. Compare classical and non-classical logic systems, including modal, temporal, fuzzy, paraconsistent, and relevance logics. Examine the philosophical foundations of logic in ontology, epistemology, and ethics. Discover the practical applications of logic in computer science, mathematics, and philosophy, enhancing your understanding of Boolean logic, programming, artificial intelligence, set theory, proof theory, and philosophical argumentation. This comprehensive guide is designed to deepen your knowledge and application of logic in various fields.
Other creations by the author
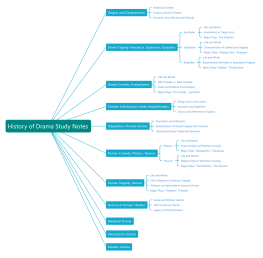
Outline/Content
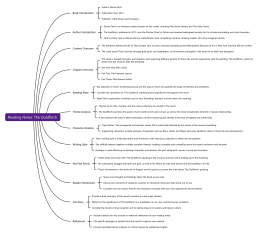
Introduction to Logic
Definition of Logic
Importance and Applications of Logic
Basic Terminology: Propositions, Arguments, Validity, Soundness
Propositional Logic
Propositions: Simple and Compound
Logical Connectives: AND, OR, NOT, IMPLIES
Truth Tables
Logical Equivalences
Predicate Logic
Quantifiers: Universal (∀) and Existential (∃)
Predicates and Variables
Logical Inference: Modus Ponens, Modus Tollens, Universal Instantiation, Existential Generalization
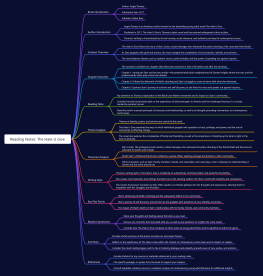
Boolean Algebra
Boolean Functions
Basic Laws of Boolean Algebra: Commutative, Associative, Distributive, Identity, Complement
Boolean Expressions and Simplification Techniques
Logical Reasoning
Deductive Reasoning vs. Inductive Reasoning
Formal Proofs: Direct Proof, Proof by Contradiction, Proof by Contrapositive
Logical Fallacies
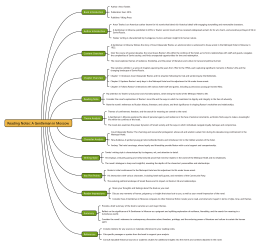
Sets and Relations
Set Theory: Sets, Subsets, Union, Intersection, Complement
Relations: Types of Relations, Reflexivity, Symmetry, Transitivity
Functions: Definition, Domain, Codomain, Range
Modal Logic
Modal Operators: Necessity (☐) and Possibility (◇)
Possible Worlds Semantics
Modal Axioms and Rules of Inference
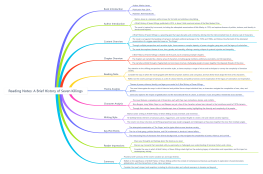
Logical Systems
Classical Logic vs. Non-Classical Logic
Modal Logic, Temporal Logic, Fuzzy Logic
Paraconsistent Logic and Relevance Logic
Philosophical Foundations
Logic and Ontology
Logic and Epistemology
Logic and Ethics
Applications of Logic
Computer Science: Boolean Logic, Programming, Artificial Intelligence
Mathematics: Set Theory, Proof Theory
Philosophy: Philosophical Logic, Argumentation
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More