Teaching Plan for Music Theory Class
2024-07-08 15:14:38 255 0 Report 0
0
Login to view full content
This teaching plan for a music theory class provides a comprehensive guide to mastering the fundamentals and advanced concepts of music theory. Starting with an introduction to music theory, it covers the definition, importance, and basic elements such as pitch, rhythm, dynamics, timbre, and texture. The plan delves into notation systems, including staff, clefs, notes, rests, and time signatures. The fundamentals of pitch are explored with detailed explanations of pitch names, clefs, intervals, scales, and key signatures. Chords and harmony are thoroughly examined, covering triads, chord progressions, seventh chords, chord inversions, and voice leading. Rhythm and meter are discussed in depth, including note and rest values, time signatures, syncopation, offbeat rhythms, polyrhythms, and cross-rhythms. Various musical forms such as binary, ternary, rondo, and sonata form are explained to enhance understanding of musical structure. Melody writing is addressed with a focus on motifs, phrases, melodic contour, sequence, variation, development, and modulation. Counterpoint techniques, including species counterpoint, imitative counterpoint, canon, fugue, and Baroque counterpoint, are also covered. Musical analysis is an integral part of the plan, encompassing harmonic, formal, score, and stylistic analysis. Ear training exercises for interval identification, chord recognition, melodic dictation, and rhythmic dictation are included to develop aural skills. Finally, the practical application of music theory is emphasized through composition exercises, arranging and orchestration, score reading and transcription, and musical improvisation. This structured approach ensures a thorough understanding and practical application of music theory principles.
Other creations by the author
Outline/Content
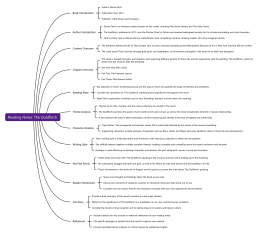
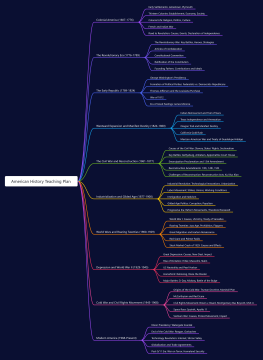
Introduction to Music Theory
Definition and Importance of Music Theory
Basic Elements of Music: Pitch, Rhythm, Dynamics, Timbre, Texture
Notation Systems: Staff, Clefs, Notes, Rests, Time Signatures
Fundamentals of Pitch
Pitch Names and Clefs: Treble Clef, Bass Clef
Intervals: Major, Minor, Perfect
Scales: Major, Natural Minor, Harmonic Minor, Melodic Minor
Key Signatures: Major Keys, Relative Minor Keys
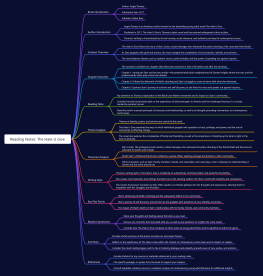
Chords and Harmony
Triads: Major, Minor, Diminished, Augmented
Chord Progressions: Cadences, Circle of Fifths
Seventh Chords: Dominant 7th, Major 7th, Minor 7th
Chord Inversions and Voice Leading
Rhythm and Meter
Note and Rest Values: Whole Note, Half Note, Quarter Note, Eighth Note
Time Signatures: Simple Meter, Compound Meter
Syncopation and Offbeat Rhythms
Polyrhythms and Cross-Rhythms
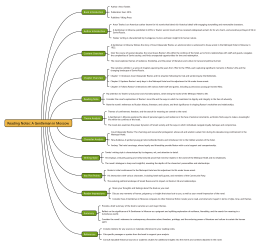
Musical Forms
Binary Form: AABB
Ternary Form: ABA
Rondo Form: ABACADA
Sonata Form: Exposition, Development, Recapitulation
Melody Writing
Motifs and Phrases
Melodic Contour: Ascending, Descending, Conjunct, Disjunct
Sequence and Variation
Melodic Development and Modulation
Counterpoint
Species Counterpoint: First Species, Second Species
Imitative Counterpoint
Canon and Fugue
Baroque Counterpoint: Bach's Two-Part Inventions
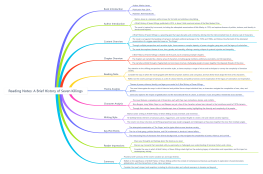
Musical Analysis
Harmonic Analysis: Roman Numeral Analysis
Formal Analysis: Structure, Themes, Development
Score Analysis: Orchestration, Instrumentation
Stylistic Analysis: Classical, Romantic, 20th Century Music
Ear Training
Interval Identification
Chord Recognition
Melodic Dictation
Rhythmic Dictation
Music Theory in Practice
Composition Exercises
Arranging and Orchestration
Score Reading and Transcription
Musical Improvisation
0 Comments
Next page
Recommended for you
More