Six Sigma is a data-based quality management method that aims to achieve near-perfect product and service standards by reducing process variation and waste, optimizing and continuously improving processes. The core idea of Six Sigma is the pursuit of "zero defects", which means only 3.4 errors per million operations.
Six Sigma includes two processes: Six Sigma DMAIC and Six Sigma DMADV. DMAIC is the process of defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling projects that are currently below Six Sigma specifications. DMADV is the process of defining, measuring, analyzing, designing, and verifying new products or projects that attempt to achieve Six Sigma quality. This article mainly discusses how to use the DMAIC model in Six Sigma to improve project management processes.
DMAIC is the most commonly used process improvement model in Six Sigma management , which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. This model provides a structured approach for teams to identify, analyze and solve problems.
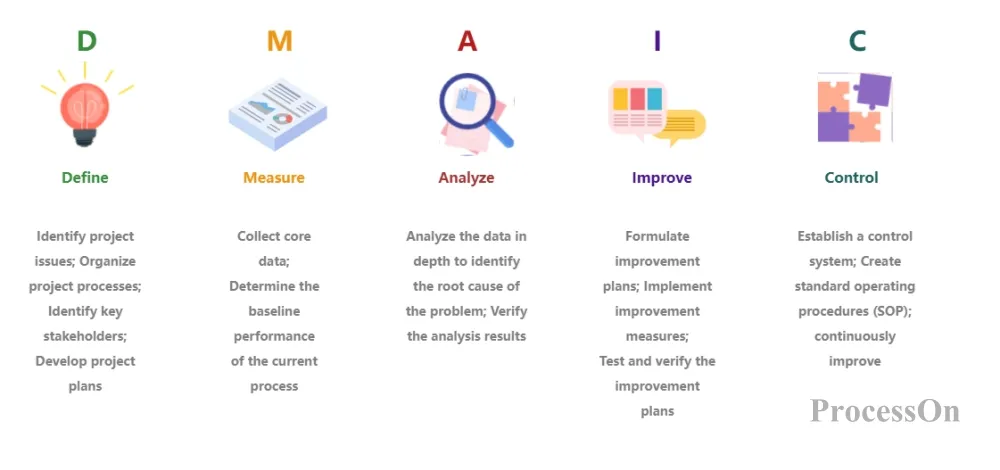
Six Sigma Project Management Improvement Method-DMAIC Model
During the definition phase, the project team needs to clarify the goals and scope of the project, identify the problem, sort out the processes to be improved, identify the needs and expectations of key stakeholders, determine key process input and output indicators (KPIs) , and output the project process.
Clarify project goals and scope , and identify problems : The project team should ensure that the project goals are specific, measurable, and consistent with the company's strategic goals. At the same time, clearly define the project scope to avoid scope creep.
Sort out the project process: Draw out the current business processes that need to be improved based on the goals.
Identify key stakeholders: including project sponsors, team members, customers, etc., to ensure their understanding and support for the project.
Develop a project plan: including timelines, resource allocation, and risk management strategies, ensuring the plan is detailed and actionable.
Example : In order to improve customer satisfaction, a network operator decided to use Six Sigma to improve the customer complaint handling process. In the definition phase, the team identified the goal of reducing the customer complaint rate, defined the scope of complaint handling, sorted out the current customer complaint handling process, identified key stakeholders (such as customer service staff, technical support team, customers, etc.), and developed a detailed project plan .
sort out the project process by drawing basic business process diagrams, swimlane diagrams , SIPOC diagrams, etc.
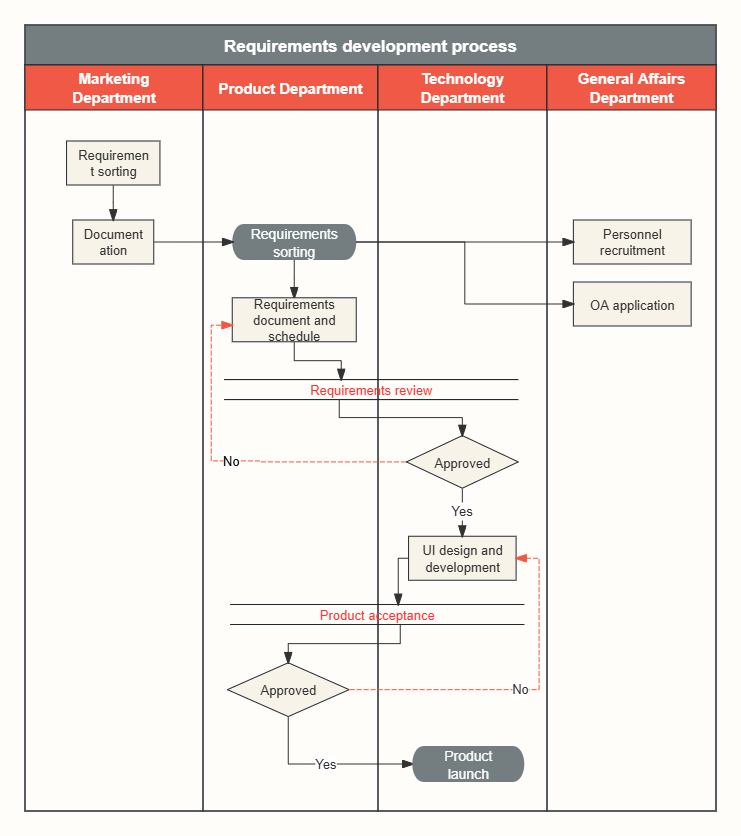
Requirements development process swim lane diagram
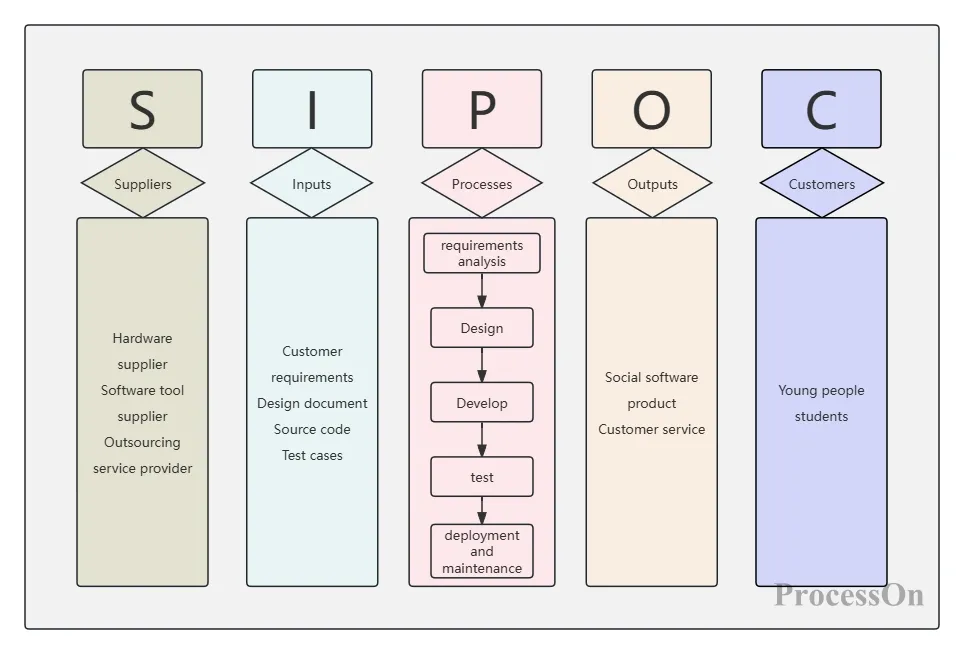
Use this template -Social software development SIPOC diagram
The core of the measurement phase is to collect data on existing processes to determine the performance and problems of the current process. First, collect core data, including key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production cycle, defect rate, and customer satisfaction. Based on the collected data, determine the baseline performance of the current process as a benchmark for improvement.
Example : In the case of the network operator mentioned above , the team collected data on the customer complaint handling process, such as complaint handling time, handling results, customer satisfaction, etc., and determined the baseline performance of the current process. At the same time, the accuracy and consistency of the measurement system were verified.
The goal of the analysis phase is to identify the root causes of process problems.
Use tools and methods: such as fishbone diagram , 5Why analysis, etc. to deeply analyze the data and find out the root cause of the problem.
Statistical analysis: Apply statistical methods to conduct in-depth analysis of data to identify patterns and trends.
Verify analysis results: Ensure that the analysis results can truly reflect the problems in the existing process and provide a reliable basis for subsequent improvements.
Example : A network operator ’s team used the fishbone diagram method to deeply analyze the problems in the customer complaint handling process and found that long complaint handling time and unsatisfactory handling results were the main reasons. Through statistical analysis, the team further confirmed the scope and extent of these reasons.
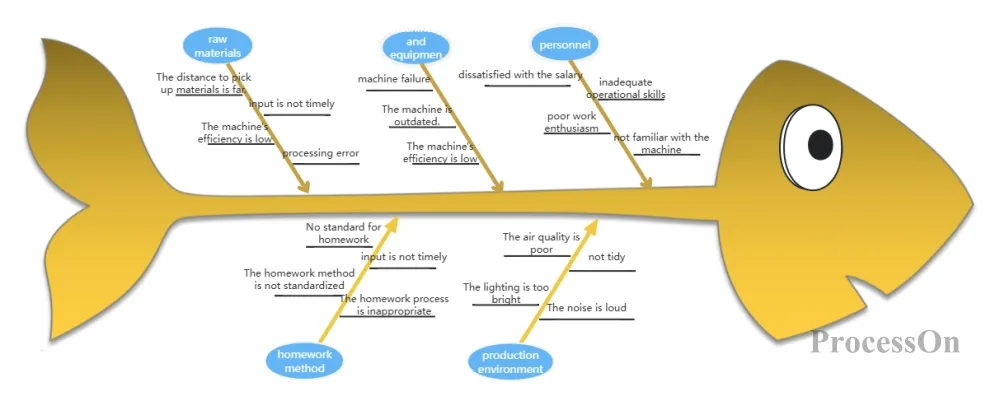
Fishbone diagram (cause and effect diagram) template
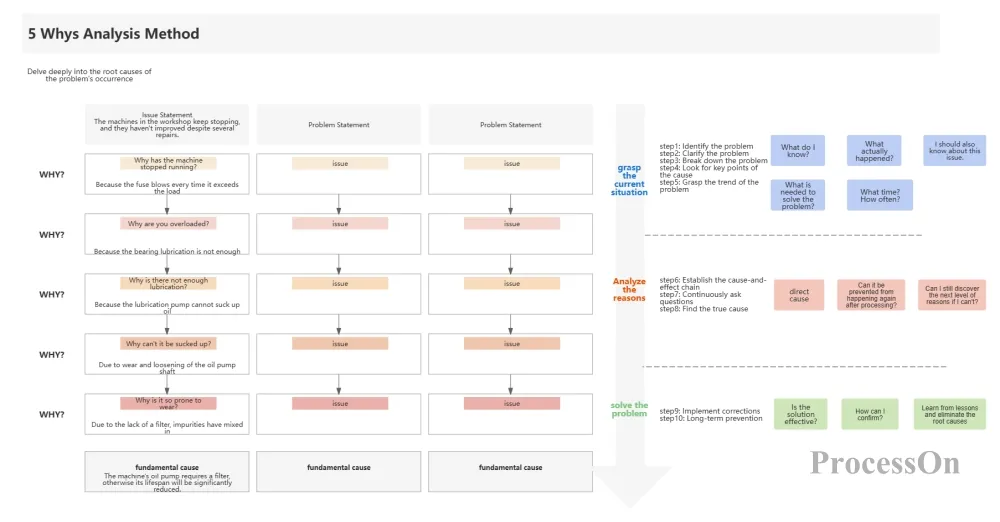
5Why Root Cause Analysis Template
The main task of the improvement phase is to develop and implement improvement measures to solve the problems identified in the analysis phase.
Develop an improvement plan: Based on the analysis results, develop a specific improvement plan, including detailed steps, required resources and expected effects.
Implement improvement measures: Implement specific improvement measures according to the formulated improvement plan, and closely monitor the effects of the improvement measures.
Testing and verification: After implementing improvement measures, conduct testing and verification to ensure that the improvement effects achieve the expected goals.
Example : The network operator 's team formulated an improvement plan to shorten the complaint handling time and improve the satisfaction of the handling results, and implemented corresponding improvement measures, such as optimizing the complaint handling process and strengthening customer service staff training. Through testing and verification, the team found that the improvement effect was significant and the customer complaint rate was significantly reduced.
The goal of the control phase is to ensure that improvements are sustained and to prevent problems from recurring.
Establish a control system: including continuous monitoring, regular review and feedback mechanisms to ensure that improvement measures are effective in the long term.
Prepare standard operating procedures (SOP) : to standardize the improved processes and ensure that team members can perform according to the standards.
Continuous Improvement: Maintain and improve the efficiency of business processes by constantly monitoring and analyzing process performance and discovering and solving new problems.
Example : The network operator ’s team established a control system for the complaint handling process, including mechanisms such as regular review of complaint handling data and feedback on improvement results. At the same time, a standard operating procedure (SOP) was compiled to standardize the improved complaint handling process. Through continuous improvement, the team continuously optimized process performance and improved customer satisfaction.
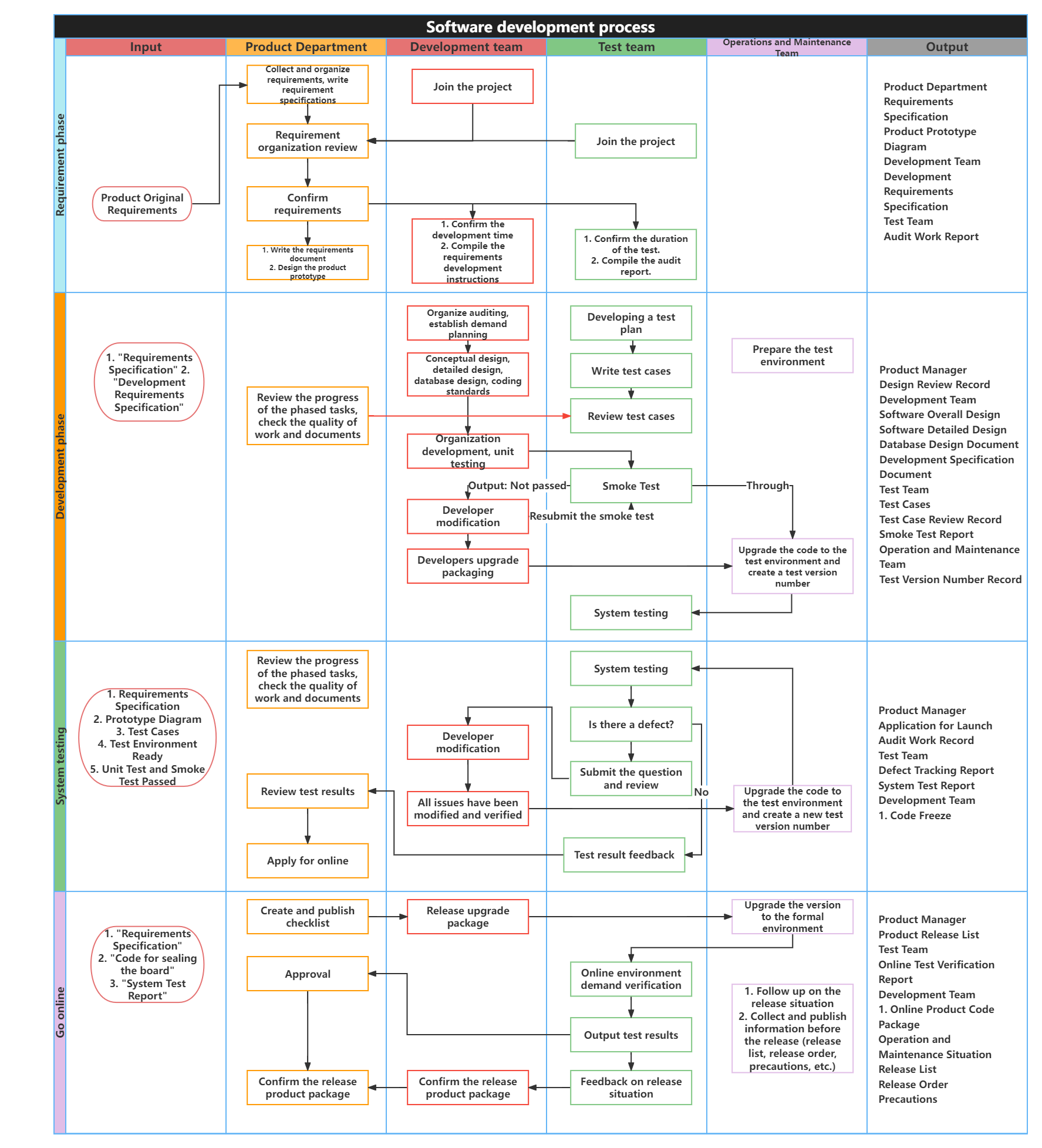
Software Development Process SOP
DMAIC in Lean Six Sigma and DMAIC in Six Sigma are essentially the same, both representing a five-stage process improvement approach of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
DMAIC in Lean Six Sigma is an organic combination of Lean Production and Six Sigma Management. It not only focuses on variation issues, but also combines the concept of eliminating waste in Lean Production, and integrates more Lean tools and methods , such as the PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act/Adjust) method , 5S management , etc. These tools and methods help to more comprehensively identify and solve problems in the process and achieve greater improvement effects.
The DMAIC process is a core component of the Six Sigma methodology, providing a clear framework for the team to implement improvements in a systematic and structured manner according to the steps of definition, measurement, analysis, improvement and control. Through this method, enterprises can solve complex problems more effectively and achieve higher quality and efficiency goals.