

Efficiently learning and building a personal knowledge system is a systematic and continuous process that plays an important role in personal growth, career development, problem solving and many other aspects.
A systematic knowledge system helps to improve learning efficiency, helping learners connect scattered knowledge points to form an organized and logical knowledge network, and can find the position of new knowledge in the knowledge system more quickly when memorizing and understanding it. Establishing a systematic knowledge system in career development can quickly mobilize relevant knowledge when facing complex problems, conduct comprehensive analysis and judgment, and help individuals better cope with challenges and problems in their work.
So the first question is, how to learn efficiently?
First, make it clear why you want to learn this skill or course. Is it for career development, hobbies, or just to broaden your horizons? A clear learning purpose can stimulate your motivation and keep you focused and passionate during the learning process.
according to the SMART principle can make them clearer.
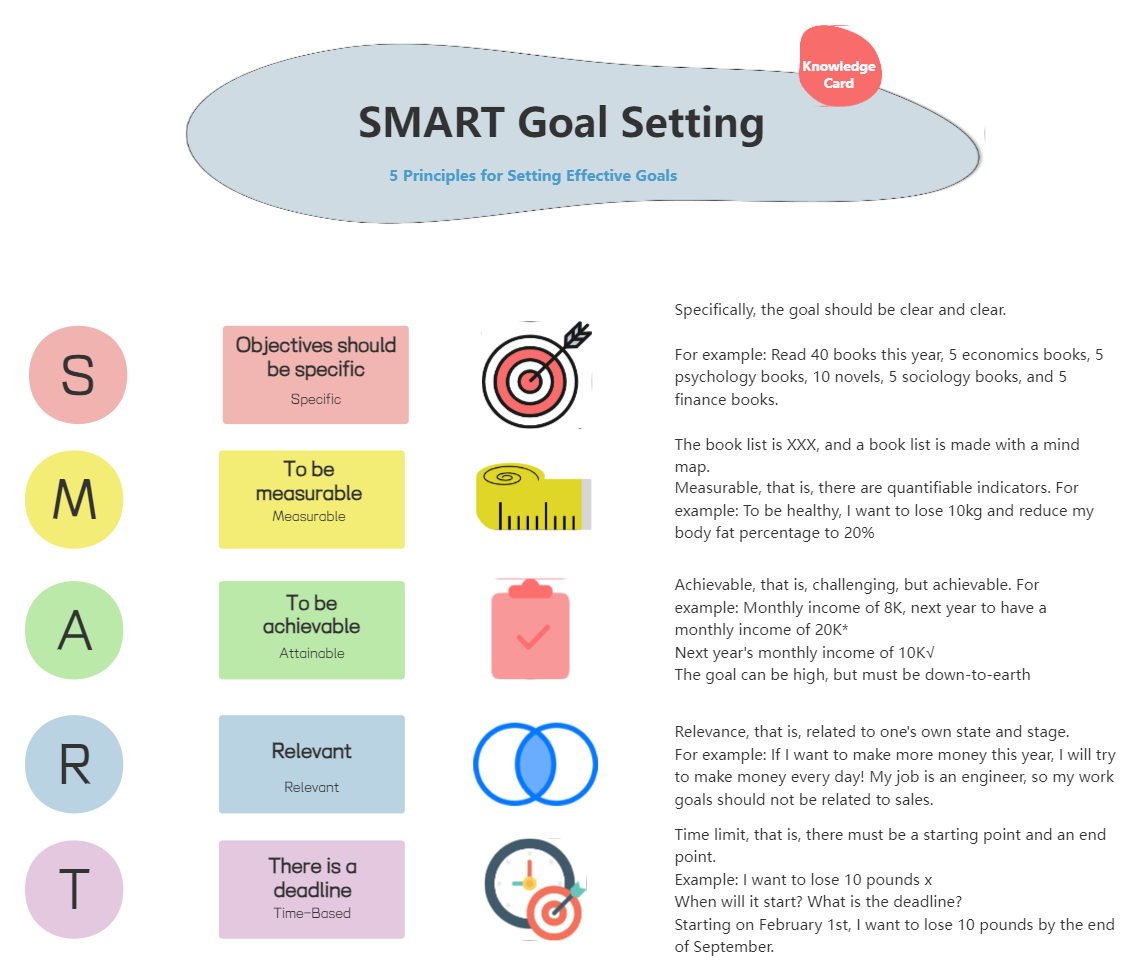
1. Break down big goals
Break down the big goal into a series of small goals or phased tasks. Each small goal should be independently achievable and gradually move closer to the big goal. For example, when learning programming, you can first set small goals such as "mastering variables and data types", "understanding control structures", and "learning functions and modules".
2. Make a detailed plan
Make a detailed implementation plan for each small goal, including learning content, learning methods, time arrangement, etc. Use a calendar or task management tool to track progress and ensure that it is executed as planned.
3. Leave room for adjustment
Plans can never keep up with changes, so when making plans, you should leave some room for adjustment. You can flexibly adjust the plan according to the actual situation to ensure the continuity and effectiveness of the learning process.
Mind Map Learning Method
When learning specific skills or courses, it is very important to build a knowledge tree, which can classify and organize knowledge points according to hierarchical relationships. It is recommended to use the mind map method to build the overall framework of the knowledge system. Mind map is a visual knowledge management tool that connects various knowledge points through graphics and lines to form a network structure. It not only helps to organize and memorize knowledge, but also stimulates creative thinking.
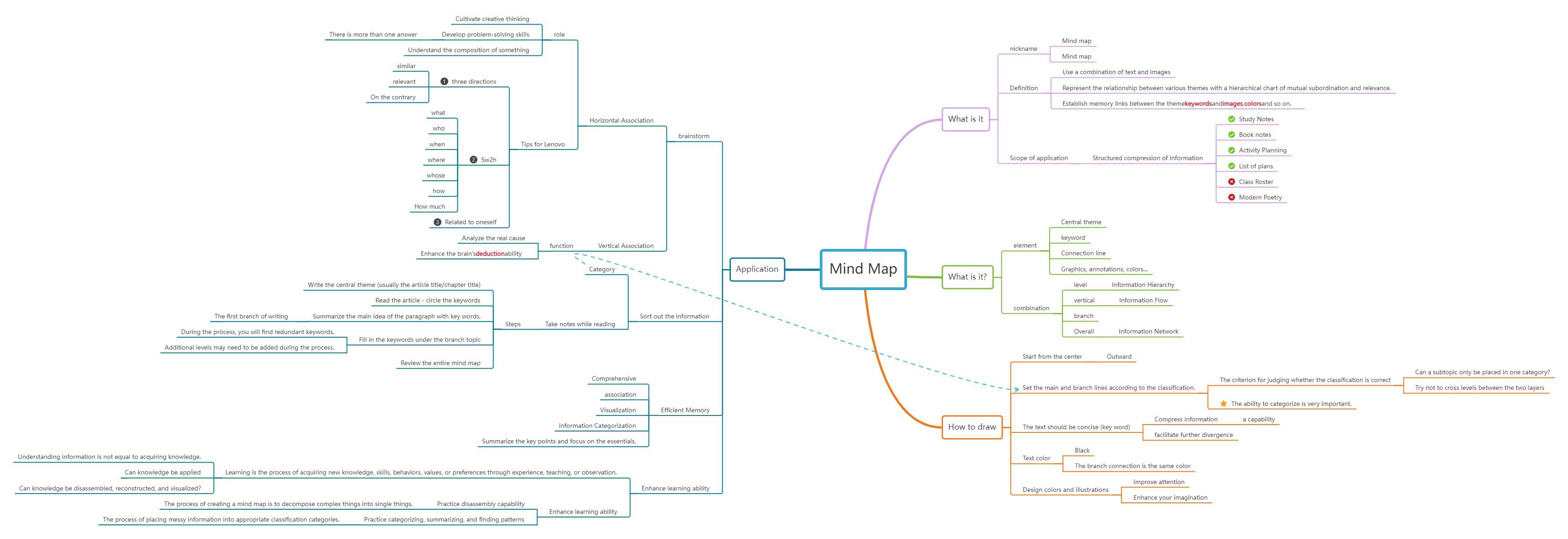
The specific steps to draw a mind map are:
Central Theme: Write the theme or core concept in the center of the paper.
Branching: Starting from the central theme, use lines and keywords to connect related sub-themes or details to form a tree-like structure.
Visualize: Use colors, icons, and images to enhance memory and understanding.
Flexible adjustment: As learning deepens, you can constantly adjust and improve the mind map.
It is recommended to use ProcessOn to create mind maps. ProcessOn mind maps are easy to operate. Branches can be created through simple shortcut keys. At the same time, icons, labels, mathematical formulas, code blocks and other forms can be inserted to complete the recording and display of knowledge points.
In addition to the mind map note-taking method mentioned above, here are two more efficient note-taking methods that are helpful for learning and memory in different scenarios:
Cornell Method
Cornell note-taking method is widely used in lectures, reading and reviewing. Its core concept is to combine note-taking with thinking, understanding, application and review to improve learning efficiency and memory.
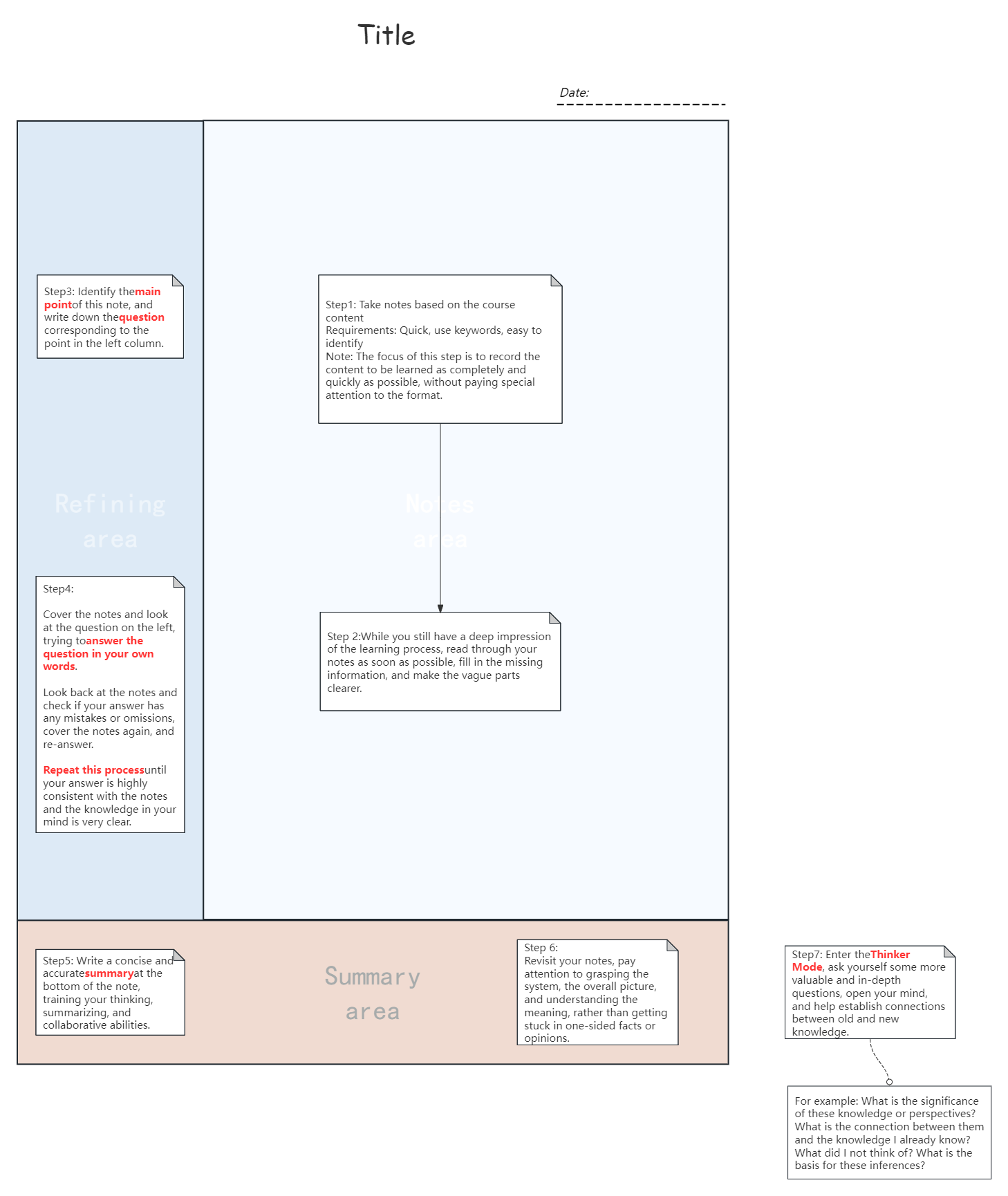
The specific steps of the Cornell note-taking method are:
Record
As you listen to a lecture or read, write down key information in the main area of your notebook (usually on the right side of the page). This information includes main ideas, concept explanations, theorems, etc., as well as some important details.
Try to be concise when recording, and use symbols, abbreviations, and keywords to speed up recording and ensure the readability of your notes.
Reduce
After class or after reading, simplify and summarize the content of the main area as soon as possible, extract key words or phrases, and record them in the left area of the page (sub-column). This process helps to deepen understanding and extract the core content.
Recite
Cover the main area and try to fully repeat the main points of the class or reading materials by relying only on the key words or phrases in the left area. This process helps to remember and consolidate what you have learned.
Reflect
In a separate section of your notebook (it can be at the bottom of the page or on a separate card), write down your thoughts, opinions, experiences, etc. These should be separated from the lecture content and have titles and indexes for easy reference. Through the thinking process, you can deepen your understanding and application of knowledge.
Review
Review your notes regularly, especially the keywords in the left area and the summary in the bottom area. By repeatedly reviewing and consolidating, you can transform short-term memory into long-term memory.
McKinsey Notetaking Method
When you encounter difficulties or confusion in the learning process, the McKinsey note-taking method can be used to help solve the problem. The core of the McKinsey note-taking method is to use notes as a "thinking tool" and a "problem-solving tool". Notes can be used to clarify ideas, discover problems, propose hypotheses and verify hypotheses, and ultimately solve problems.
The McKinsey note-taking method emphasizes the goal of achieving results. Notes are not just for yourself to read, but also need to be able to be clearly communicated to third parties (such as superiors, colleagues, and clients).

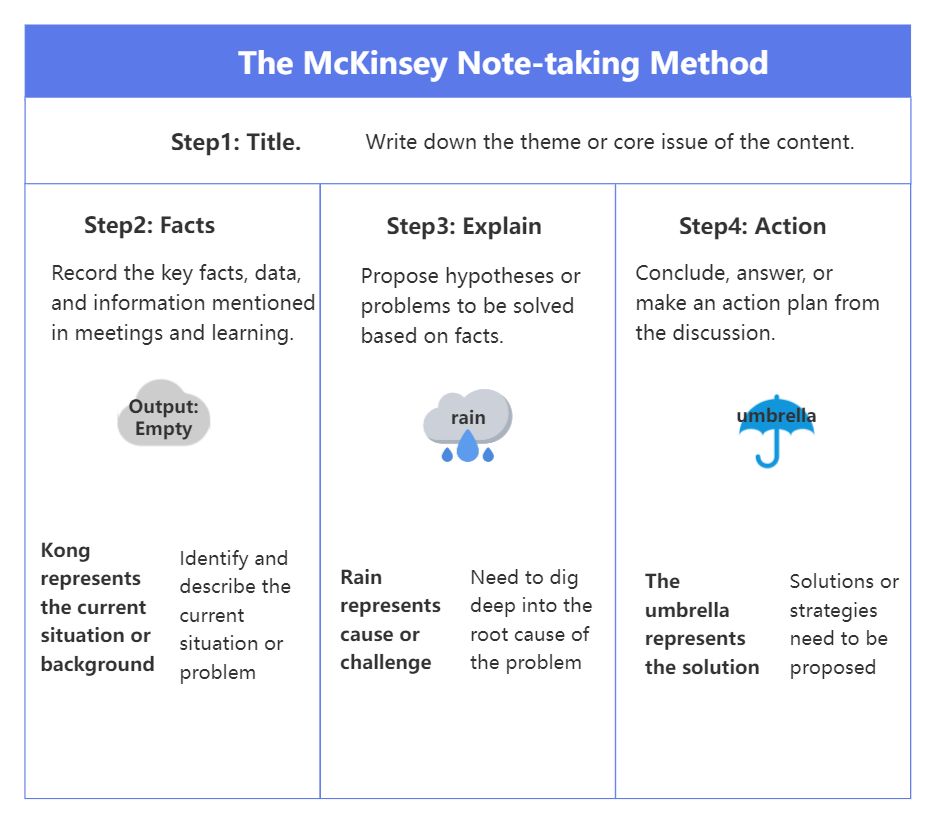
The specific steps of the McKinsey note-taking method are:
Use the notebook in landscape orientation: A4 paper uses one side, B5 and smaller paper uses left and right sides combined into one page.
Control the color of your handwriting: It is best to use blue for taking notes and red for revisions or key points, as blue can stimulate thinking and creativity.
Divide into areas: Divide your notes into fact area, explanation area and practice area to record facts, thoughts and solutions respectively.
Golden Trisection: Follow the trisection principle of "facts → explanations → actions" to organize the content of your notes.
At the knowledge review stage, the Feynman learning method can be used to consolidate learning outcomes.
Feynman Learning Method
By expressing complex concepts or knowledge in simple and clear language, learners are required to have a deep understanding and paraphrase what they have learned. This paraphrase process not only helps learners digest and consolidate what they have learned, but also can test the results of learning and find deficiencies, providing a basis for further learning.
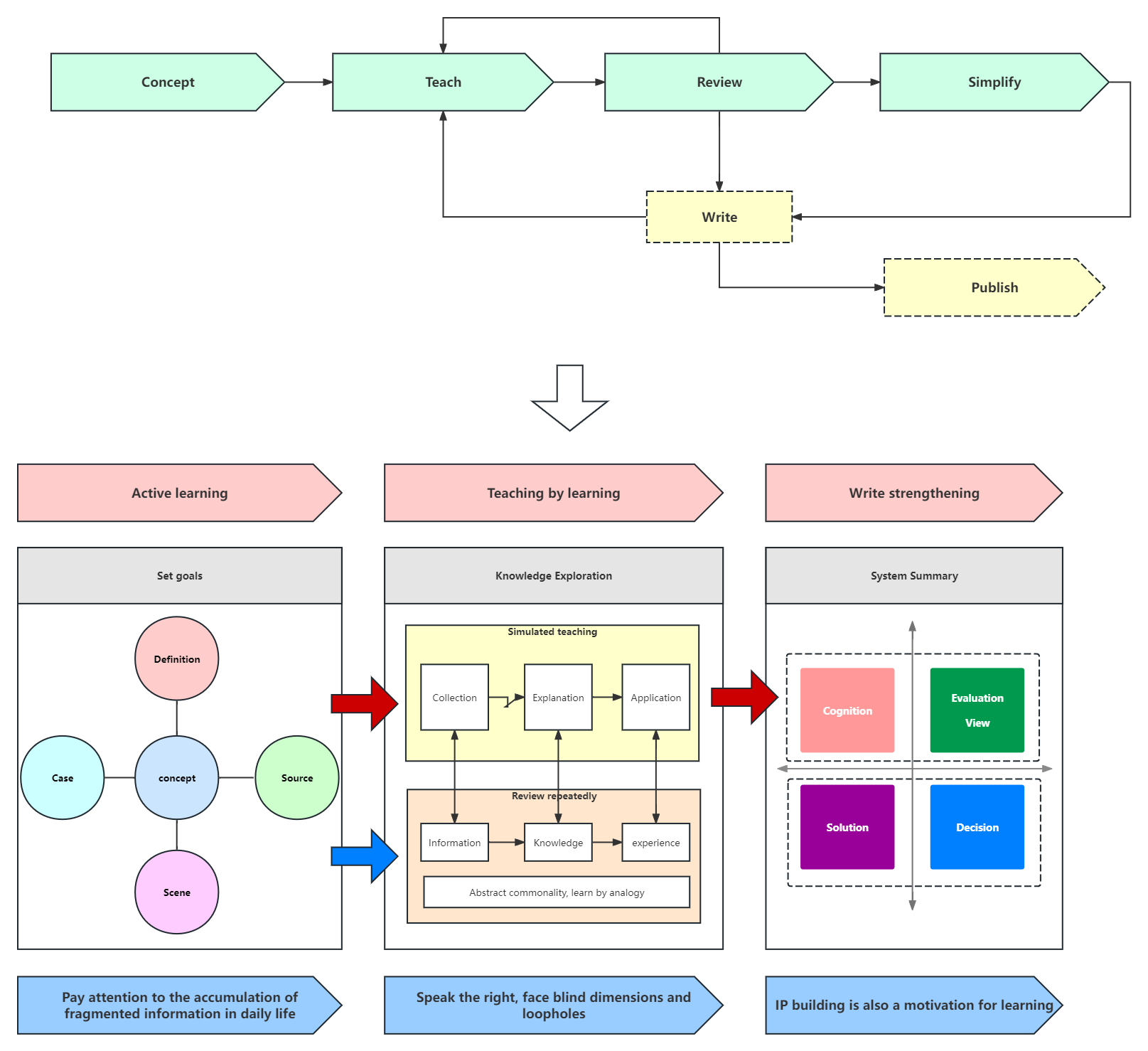
The Feynman learning method usually includes the following core steps:
Establish learning goals:
Before starting to learn, clarify the meaning and goal of learning. Learning should not be passive obedience and utilitarian-driven input, but conscious and active learning.
Establish specific, measurable, achievable, meaningful and time-bound learning goals based on personal interests and needs.
Understand what you are going to learn:
Gain a systematic understanding of the knowledge to be learned, including summarizing, screening and analyzing knowledge.
Use tools such as mind maps to help organize the knowledge framework, visualize the knowledge, and facilitate understanding and memory.
Teaching instead of learning, using output instead of input:
Try to explain what you have learned to others or yourself in a simple and understandable way. This step is the core of the Feynman learning method, which tests and consolidates what you have learned through output.
You can use scene simulation, self-talk, recording playback and other methods to retell to ensure that you can express what you have learned clearly and accurately.
Review and reflection:
After retelling the knowledge, review and reflect, check whether your explanation is correct, examine whether there are any problems with the knowledge, and summarize the experience and lessons learned.
By comparing data and facts, re-verify the relevance and correctness of knowledge and further deepen understanding.
To simplify and absorb knowledge:
After multiple repetitions and reflections, try to explain what you have learned in a more concise way to make it easier to understand and remember.
The simplification process is not only a refinement of knowledge, but also an improvement of one's own understanding.
In summary, efficient learning and building a systematic knowledge system first require clear goals and directions, formulate feasible implementation plans, use tools such as mind maps to connect scattered knowledge points into a network, form a clear knowledge structure, and conduct regular reviews so that we can quickly mobilize relevant knowledge and conduct efficient analysis and solutions when facing complex problems . At the same time, in the process of learning, we try to avoid being complacent and actively participate in online and offline discussions and exchanges. Through communication with others, we can obtain different perspectives and insights and expand our thinking.
I hope the learning tips I shared today can be helpful to everyone. The above templates are all from the ProcessOn template community . Follow ProcessOn to get more learning tips and useful information!