As a structured method, EPC can accurately describe the events, functions and logical relationships in the business process . It not only provides a visual way for the business process, but also supports the analysis, simulation and optimization of the process. Through EPC, managers can clearly see the overall picture of the process, thereby discovering potential problems and improvement opportunities. At the same time, EPC also provides a common language, making communication across departments and organizations easier and more efficient.
This article mainly starts from the concept, basic elements , drawing methods and real cases of EPC in daily work, to give you a comprehensive interpretation of EPC. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
EPC (Event-Driven Process Chain) is a method for modeling and analyzing internal business processes in an enterprise. It was proposed by German computer scientist Professor August-Wilhelm Scheer in the early 1990s and has been widely used in SAP.
EPC is a graphical modeling language that organizes static resources in the business process (such as systems, organizations, data, etc.) into a dynamic model to complete specific tasks or processes.
EPC consists of a variety of components, among which events, functions, and logical connections are more common and standardized, while other components have slight differences in different tools.
1. Event
An event represents an action or state change that occurs in the system. It is the starting point or node that triggers the flow of business processes and is usually represented by a hexagon.
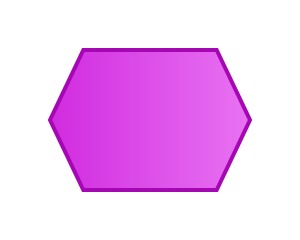
Events can be generated internally, such as a user submitting an order, inventory reaching a warning line, etc.; they can also be triggered externally, such as receiving a customer request, market changes, etc.
Events are usually subject-predicate structures, such as order arrival, cost calculation completion, etc.
2. Function
Function represents the response to an event, that is, the operation or activity to process an event. It is the core execution unit in the business process. Function implements the specific operation of the business process and is the concrete embodiment of business logic. It is usually represented by a rounded rectangle.
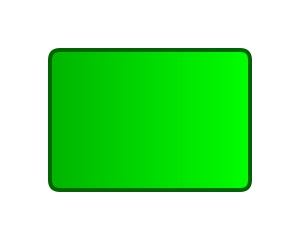
Functions can be performed by members of an organizational unit (e.g., employees, departments) or automatically by the system (e.g., through software applications).
Function descriptions are usually expressed using verb-object phrases, such as entering an order or calculating costs, to avoid using vague single verbs.
3. Logical Node
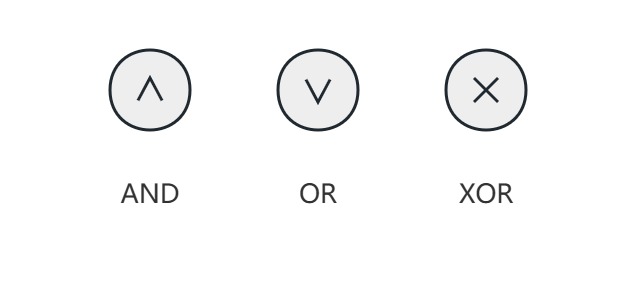
Logical nodes include: ANG node, OR node, and XOR node.
1) AND Node: All input branches must be executed before continuing.
2) OR Node: You can continue after any input branch is executed.
3) "XOR" node: Only one input branch can be executed before continuing.
4. Data/Information (Information Resource)
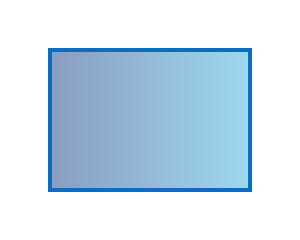
Information represents the data information needed to complete a function. It can be either the input or the output of a function. It plays an important role in the business process, transmitting necessary data and information to ensure the correct execution of functions and the smooth progress of processes. It is usually represented by a rectangle.
5. Connection Line
Used to indicate the connection between events, functions and logical nodes. Arrows indicate the direction of the process.
6. Organization Unit
Organizational units represent organizational structures or members, such as departments, teams, or individuals, that are responsible for performing functions or tasks. In the EPC model, organizational units are clearly identified so that it is clear which functions or tasks are performed by which organizational units.
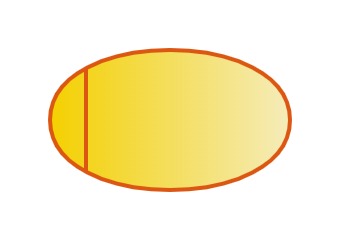
7. Process Path
The process path expresses the connection relationship between processes.
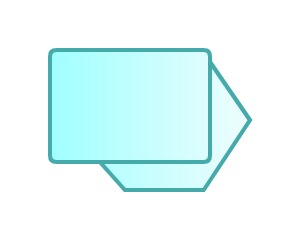
8. System
An information system that carries a certain process.
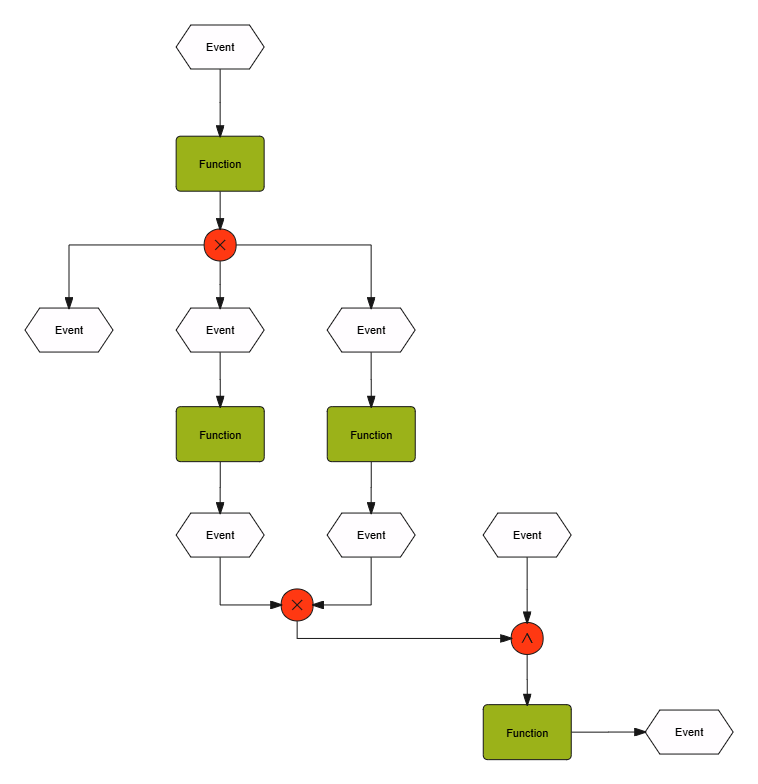
1. Event-Function-Event: The EPC model usually follows the structure of event-function-event, that is, an event triggers a function, and the completion of the function triggers the next event.
2. Closed-loop structure: The EPC model usually forms a closed-loop structure , which means that a complete business process is formed from the start event to the end event.
EPC has room for use and value in multiple industries and scenarios. Here are a few examples:
1. Process optimization : The EPC model can help companies identify bottlenecks and ineffective activities in the process and optimize them.
2. Decision support : By simulating different business scenarios, the EPC model can provide decision support to management.
3. Training and documentation : EPC models can be used as training material to help employees understand business processes.
4. System integration : The EPC model can also serve as the basis for system integration, guiding the connection and interaction of different IT systems.
ProcessOn is a professional drawing tool that supports drawing EPC diagrams, flow charts, mind maps and other professional graphics. The EPC drawing method is divided into 5 steps from the initial preparation to the final completion. The following are the detailed steps.
Step 1: Clarify the specific scope of the business process to be modeled and determine the purpose of modeling, such as process optimization, problem identification , etc.
Step 2: Identify key elements . Find out the important events in the process, including the start event , end event, and intermediate events; clarify the functions or tasks required to complete the process; determine the logical relationship between events and functions, etc.
Step 3: Create a new flowchart, check [Event Process Chain] in [More Graphics] in the lower left corner, and add related graphics to the graphics library .
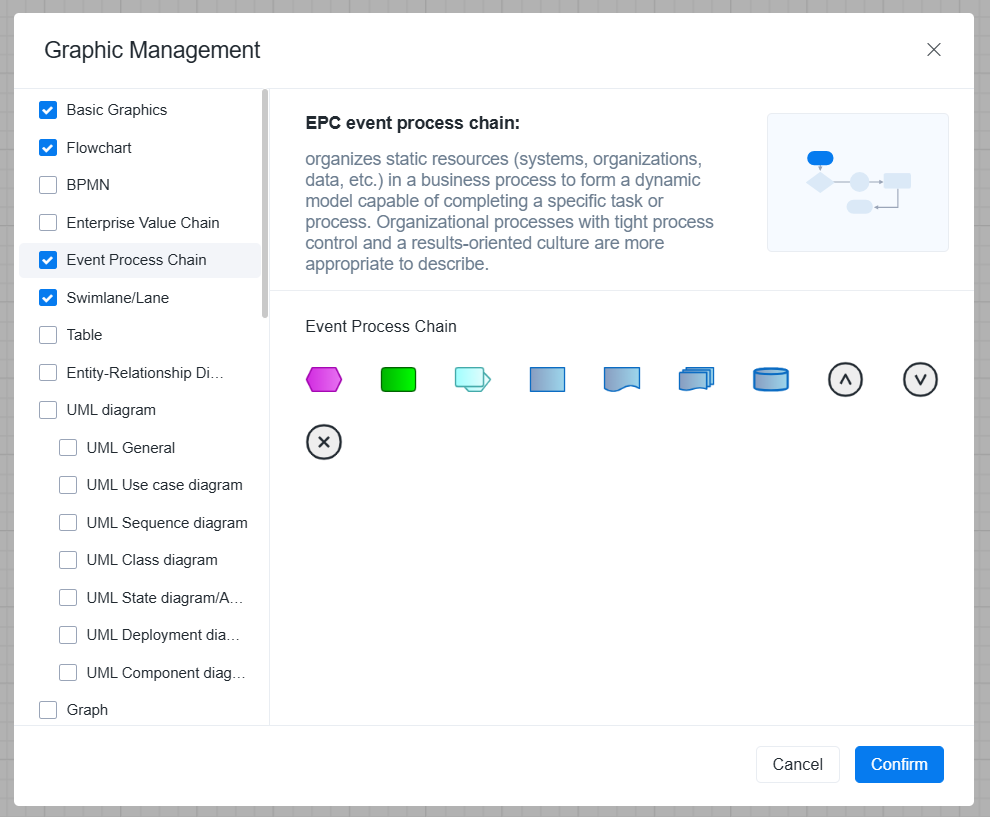
Step 4: Draw a preliminary model. Design the layout of the model based on the collected information and identified key elements; use corresponding graphic symbols to represent events, functions, and logical nodes.
Step 5: Review and improve. Team members review the draft to see if there are any omissions or errors, and then make necessary adjustments and modifications based on the feedback.
Next, I will share a few EPC user cases to help you understand the previous information and enable you to quickly and efficiently master the method of drawing EPC diagrams .
1. Goods Receiving Processing EPC
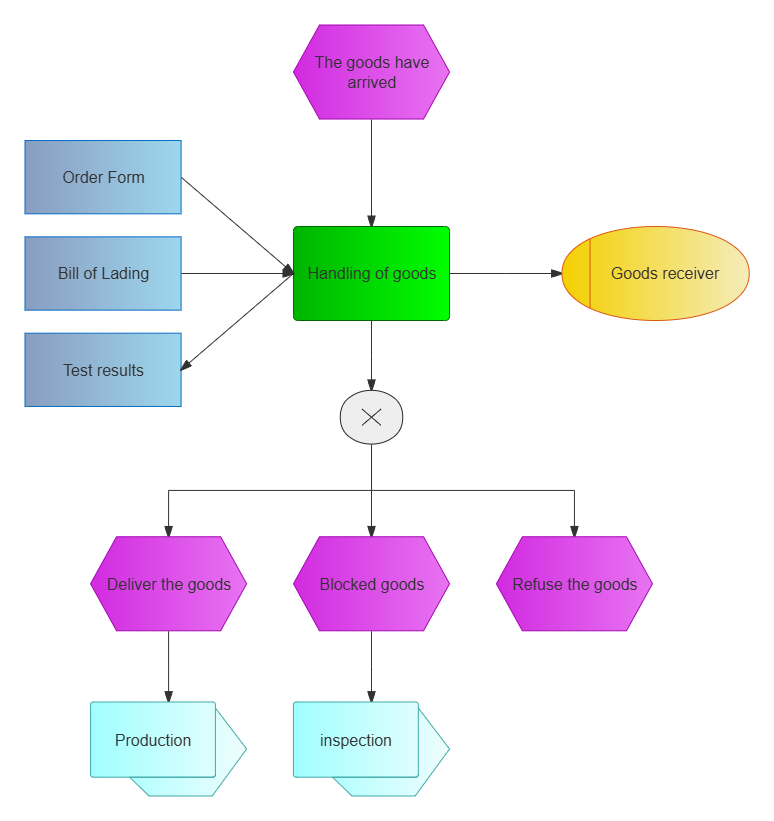
Handling of goods received EPC
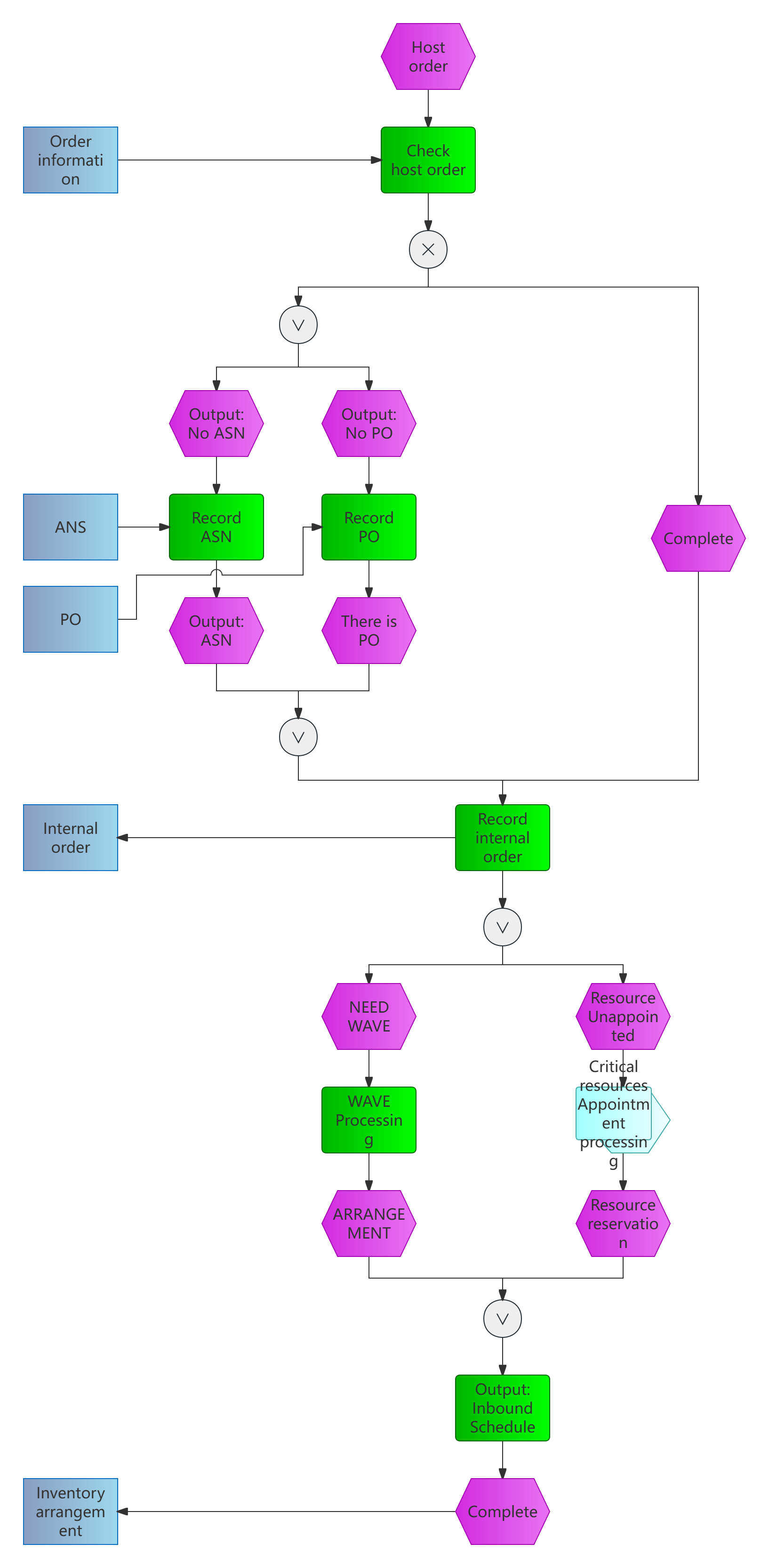
2. EPC for incoming orders
3. Maintenance process EPC diagram
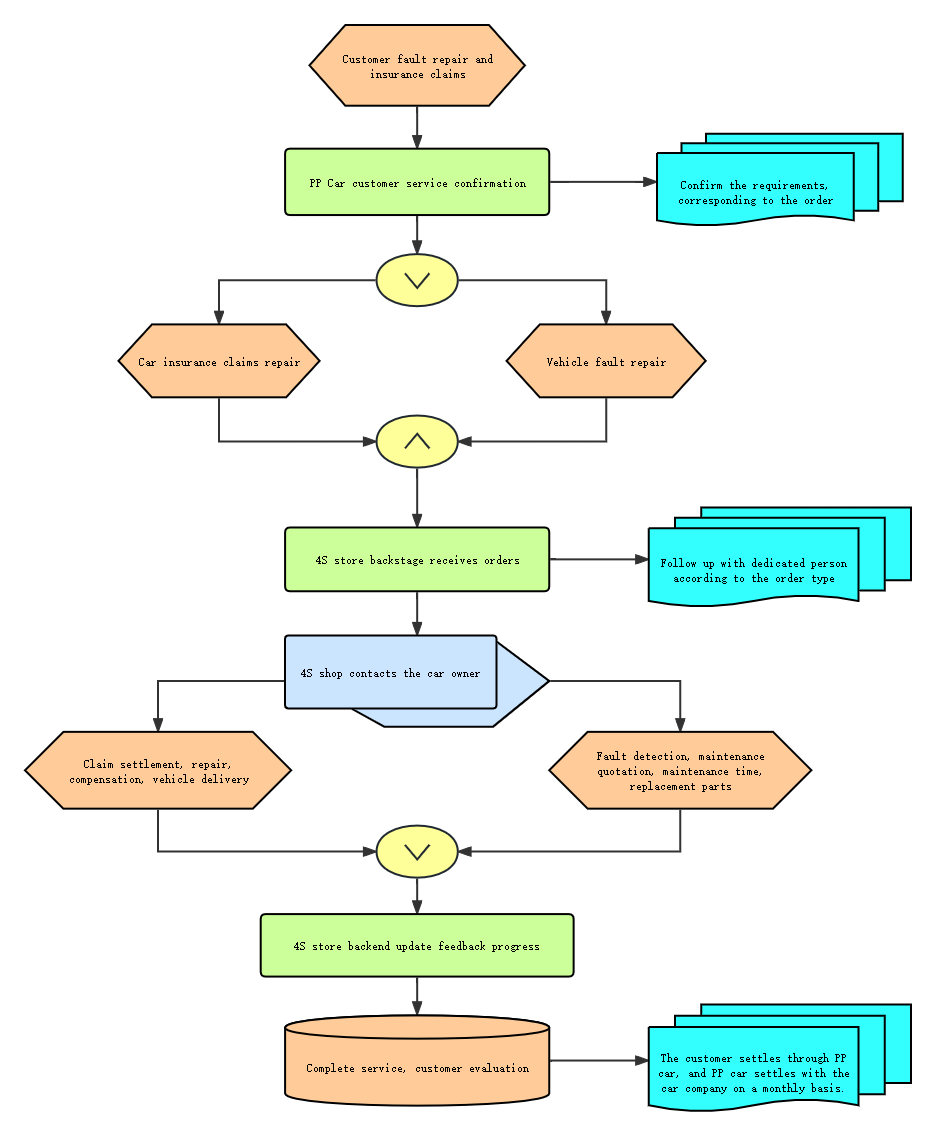
Car Insurance Recommendation Repair Process Flowchart
4. Project ManagementEPC
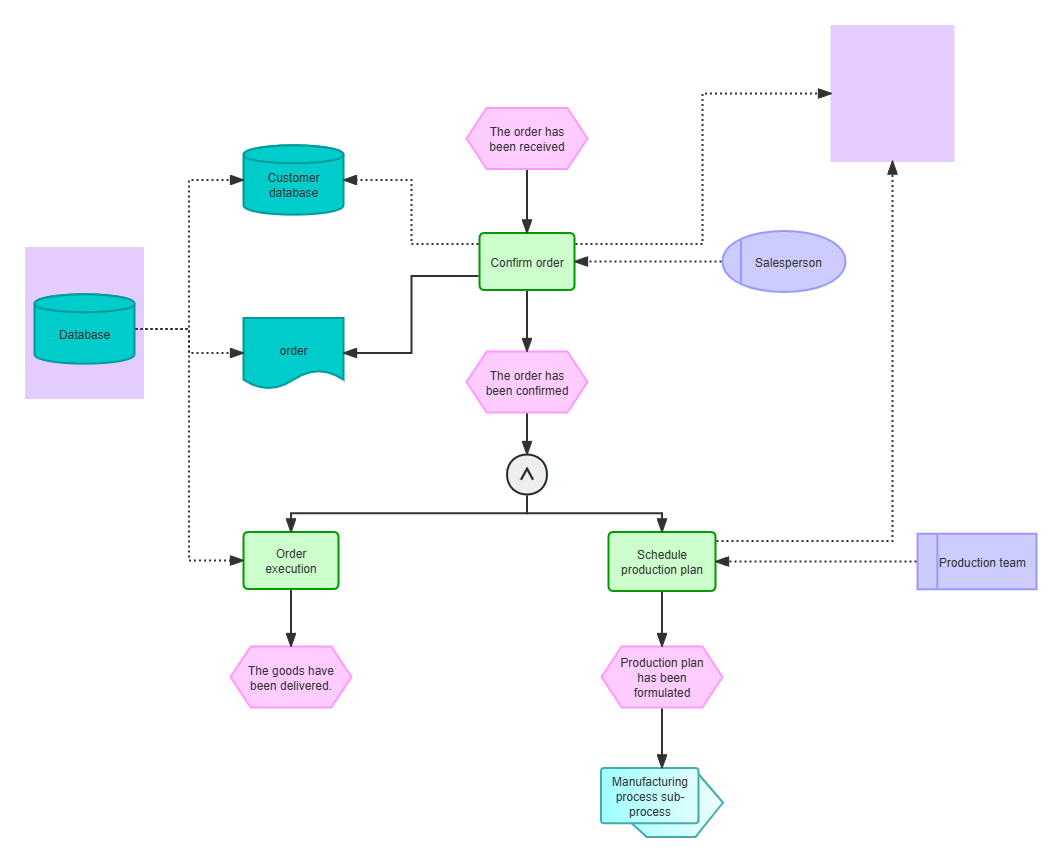
Through the introduction in this article, we not only learned the basic information of EPC and its importance in modern enterprise management, but also learned how to draw it.
As a powerful graphical modeling tool, EPC provides a clear perspective for describing, analyzing and optimizing business processes. It not only helps enterprises identify and solve bottleneck problems in the process, but also promotes communication and collaboration between departments, ultimately promoting the overall efficiency and competitiveness of the enterprise.