

As Internet products become more and more abundant, companies begin to seize limited user resources, and user demands begin to become more and more precious. It is not an exaggeration to say that "user experience is a business opportunity." Since user experience is so important, today we will discuss how UX designers improve product user experience from the basic concepts of user experience, the five elements of user experience, and user experience chart tools .
1. What is user experience?
User experience (UE/UX) is a subjective feeling that users develop when using a product. It is reflected in subtle details, but is very important.
2. Experience classification
1)Sensory experience: audio-visual experience, emphasizing comfort, including color, sound, text layout, etc.
2)Interactive experience: the experience of the interface during user use and communication, emphasizing interactive and interactive features. The interactive experience runs through the browsing, clicking and other processes.
3)Emotional experience: Give users a psychological experience, emphasize psychological recognition, and allow users to identify and express their inner emotions through the site.
3. Design goals
1)Useful: It truly meets the needs of users, has useful functions, complete content, and is helpful to users. In any scenario, the usefulness of the product must be ensured first, which is the basis of user experience.
2) Ease of use: The product is easy to use and easy for users to operate, understand, and learn. Ease of use is the "user cost". Users need to learn, spend energy, and time to use any product. Ease of use is to reduce the "user cost".
3) Easy to use: Every design pays attention to user emotions, making users feel comfortable and satisfied when using the product.
The User Experience Element Model includes five elements: strategy layer, scope layer, structure layer, framework layer and presentation layer. The following details the important role of these five elements in user experience.
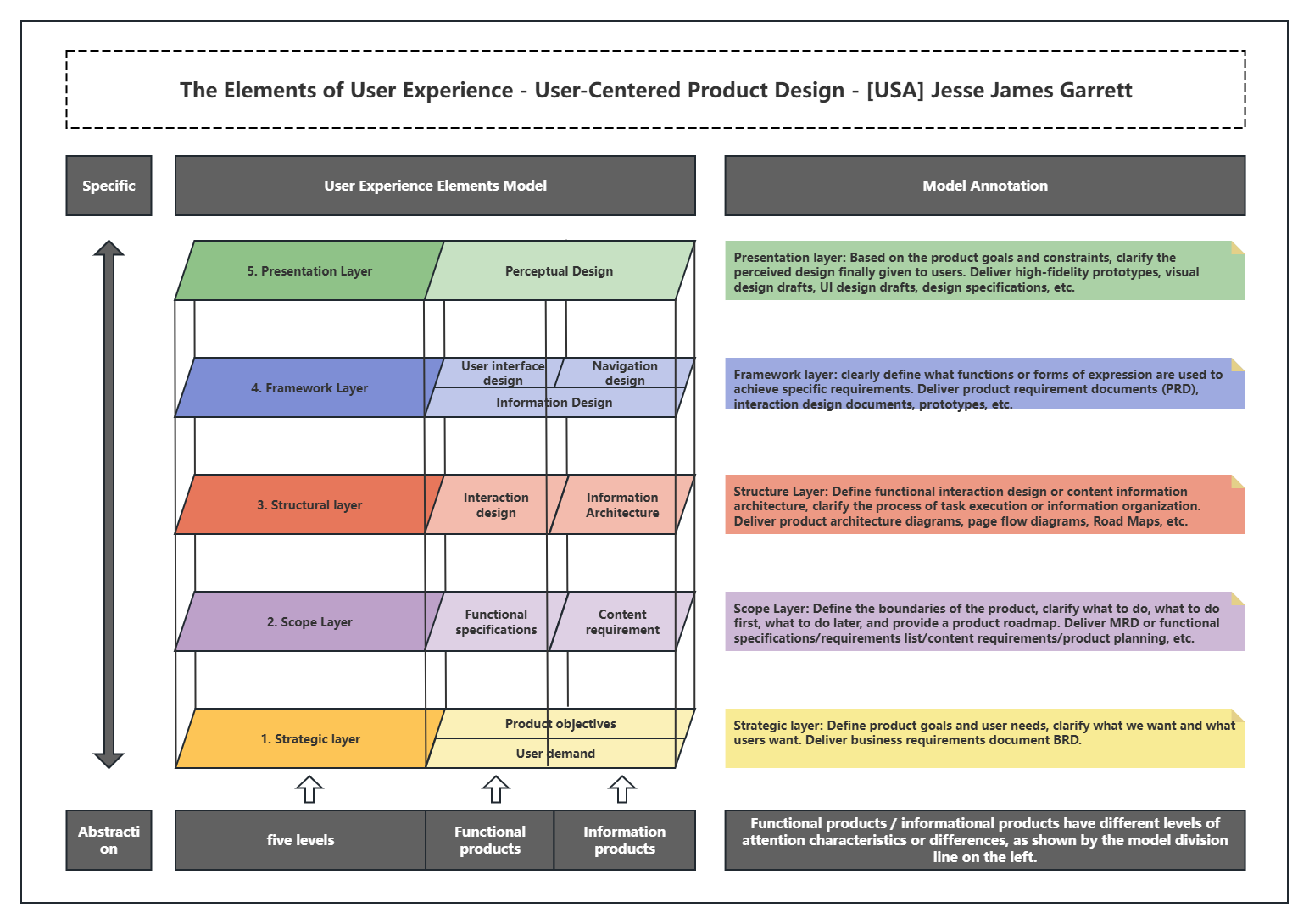
User Experience Elements-User Experience Model
1. Strategic user needs
What can users get from the product? You can analyze different user groups through specific methods such as market research, field surveys or user testing.
Product goals: What can the company get from the product?
2. Scope layer
functional specifications: Determine the priority of the function list and describe the function flow.
Content needs: Determine the priority of the content list and describe the content order.
The scope layer is generally determined by the user needs of the strategic layer. The needs are extracted from user analysis. How to convert the needs into functions is a crucial step.
3. Structural layer
interaction design: Define the interaction mode between users and products.
Information architecture: Focus on how to convey information to users, focusing on designing organizational classification and navigation structure.
4. Framework layer
interface design: buttons, input boxes, bar tables, text boxes, single and multiple selections, etc. Navigation design: Guide users to get to where they want to go as soon as possible.
Information design: How information is organized and presented on the interface.
The basic principle followed by the framework layer is to let users see the content they need and the content we want them to see first.
5. of the presentation layer
color contrast, layout, font size, icon selection, etc.
The first place the user comes into contact with must not only meet the comprehensive goals of product function, content, and UI, but also give the user a better perception.
When designing a product, you can use some models and tools to evaluate and improve the user experience. Here are four tools: User Empathy Map, User Experience Map, User Journey Map, and Service Blueprint.
1. User Empathy Map
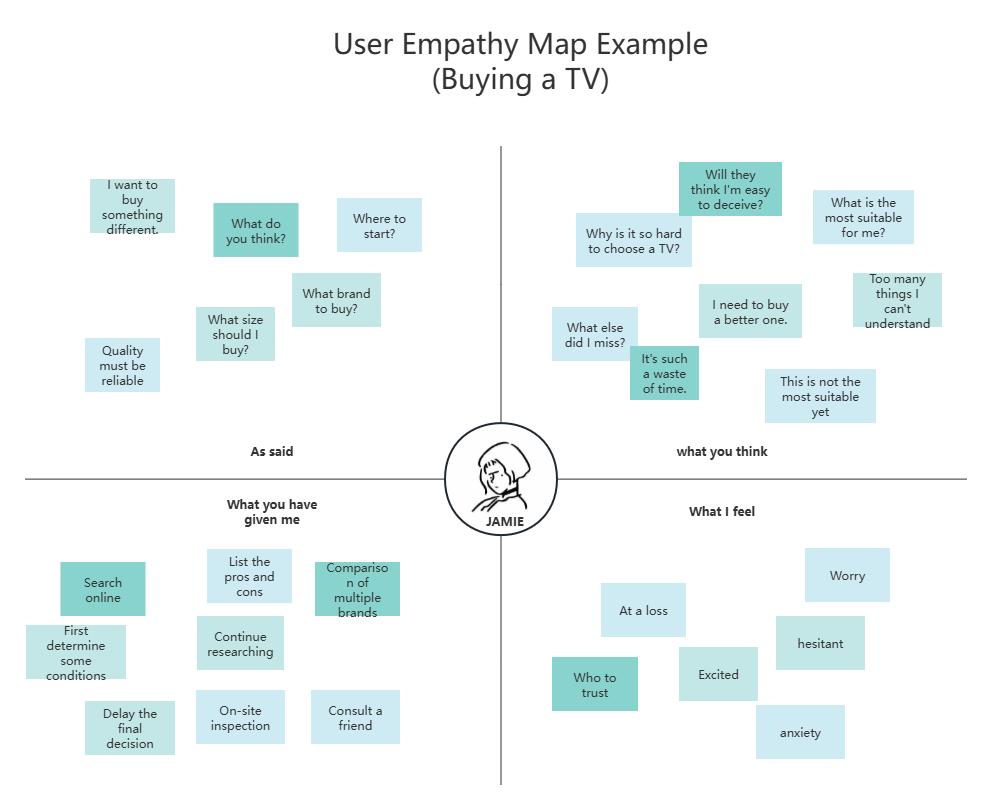
1)What is an empathy map? It qualitatively describes the user experience of a certain type of user by studying their behavior and psychological activities when using the product. It is generally used in the early stages of product design or when classifying the research results of user interviews.
2) Key elements of user empathy maps
The four key elements of empathy maps are: what users say, think, feel, and do when using the product.
3) Empathy Map Operation
Step 1: Determine the scope of a certain type of user and the mapping goal
Step 2: Collect information and user data
Step 3: Sort the cards into what you said, thought, felt, and did
Step 4: Summarize user pain points and product goals
Step 5: Optimize product design
2. User Experience Map
Case 1: User experience map of a city
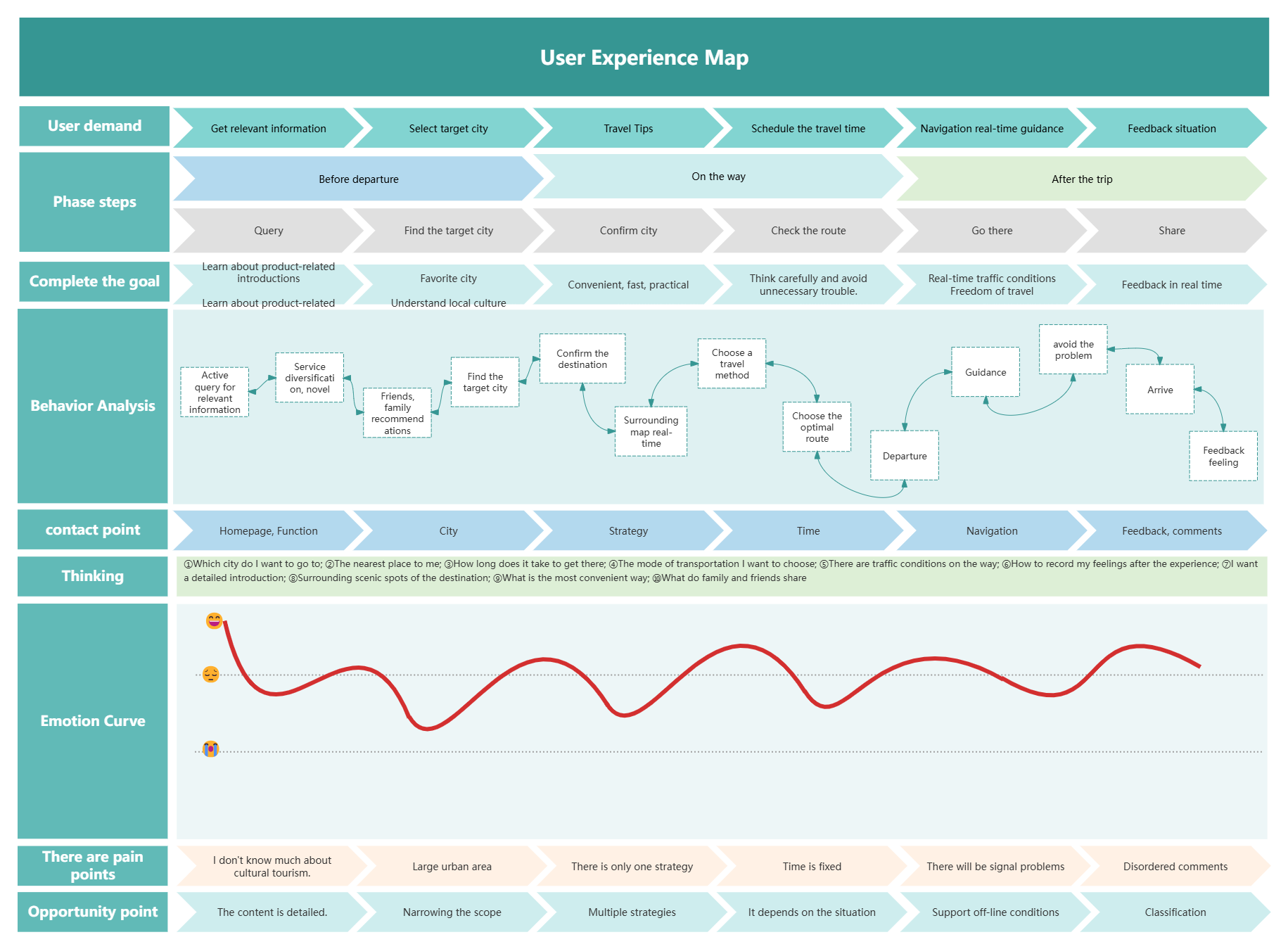
User Experience Map-Tourism Products
Case 2: Browsing the News APP User Experience Map
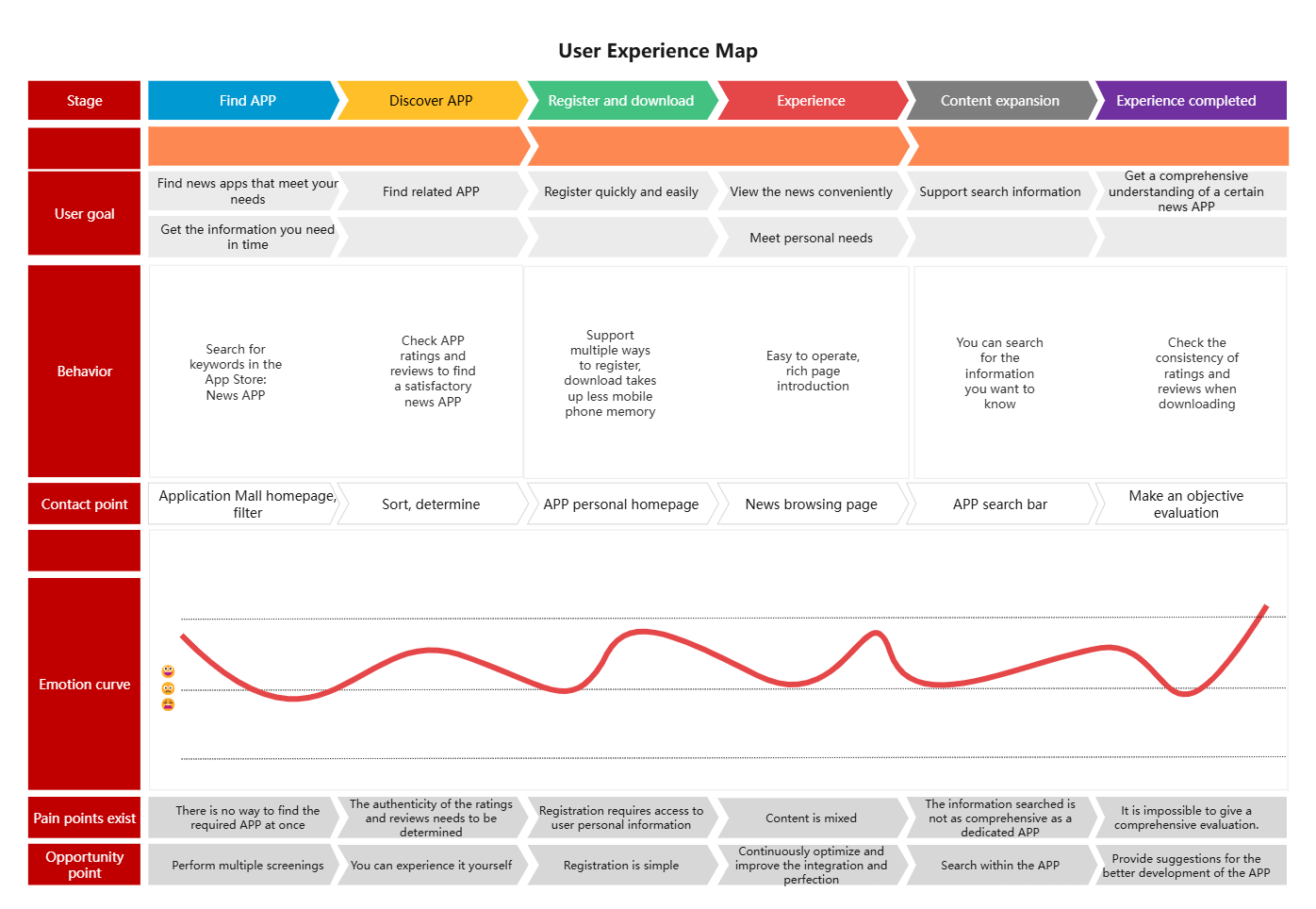
User Experience Map-News Products
1)What is a user experience map?
From the user's perspective, it describes the entire process of using a product or receiving a service from the beginning to the achievement of the goal in a storytelling way. The entire process is expressed and displayed in a visual graphic way.
2) Key elements of the user experience map
Behavior: what the user needs to do to enter the next step
Thoughts: what the user thinks during the operation
Pleasure points : where the user feels pleasant and the experience exceeds expectations
Pain points: where the user feels frustrated and the user experience is destroyed
Opportunity points: solutions discovered through pain points.
Emotional curve: score calculation
3) Operation steps
Step 1: Identify the user. Select according to the experience goal, and give priority to users with high value and long-term benefits to the product.
Step 2: Confirm the scenario. Walk through the product from the user's perspective, sort out the core scenario path from product entry to exit, sort out the coarse-grained story scenario table, and summarize the touchpoints.
Step 3: User interviews. Collect the specific behaviors, perceptions, and emotions of real users at each stage.
Step 4: Draw an experience map. Organize all interviewed user records and output them visually.
4) User Experience Map Template
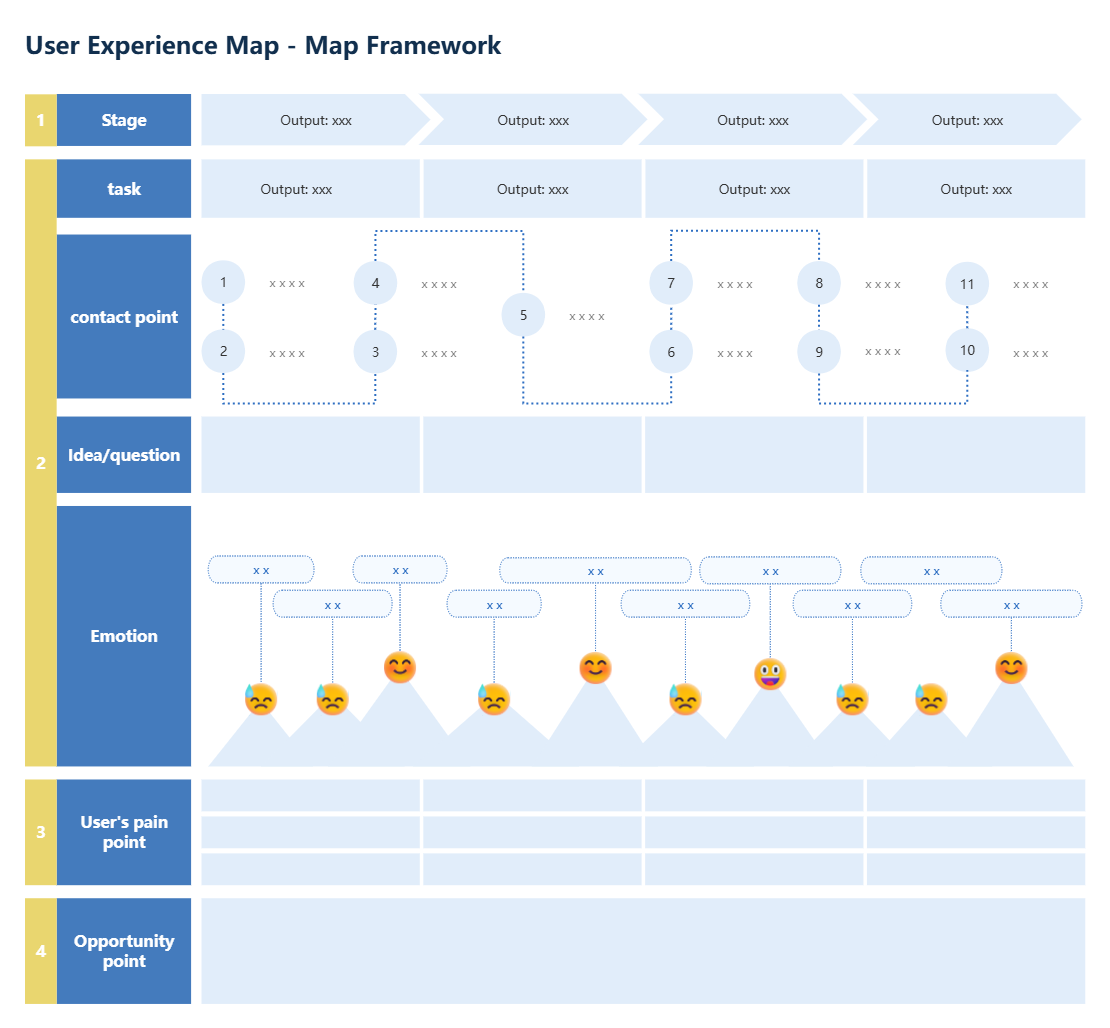
User Experience Journey Map Framework
3. User Journey Map
What is a journey map? It is what a specific user does and thinks in chronological order when using a product to complete a specific task or achieve a specific goal. The role of the user journey is to go deeper into a product module than the user experience map, and to allow designers and other relevant personnel to understand the more detailed parts of the product through this method. It can be used throughout the entire product design stage and can serve as an important reference for user needs.
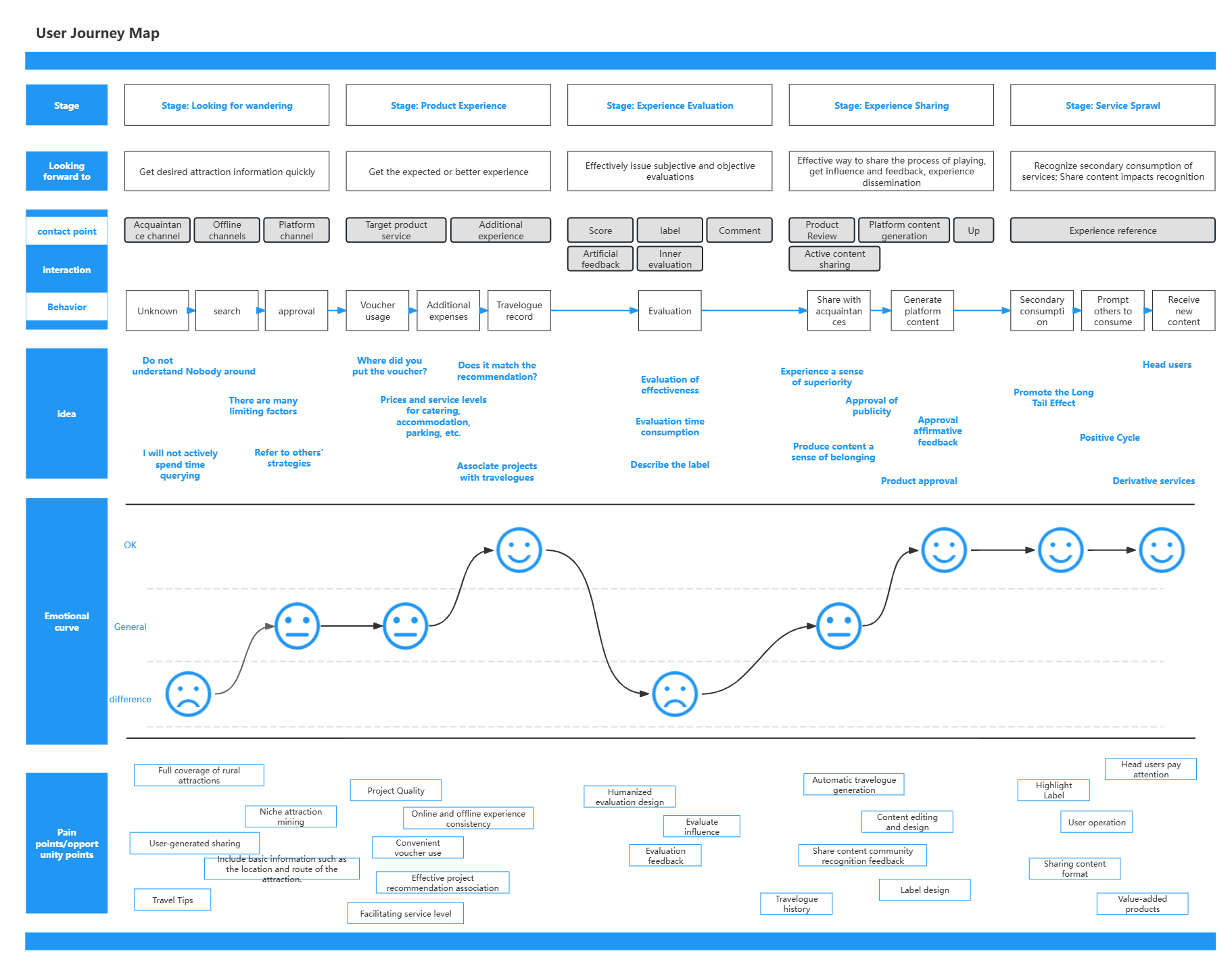
User Journey Map-Travel Products
1)Key Elements of a Journey Map
Persona: The user or persona of a journey map, which is closely related to the journey map, and the user's behavior is deeply rooted in the data.
Scenario + Expectation: The problem that the journey map needs to solve.
Journey Stage: The high-level stage experienced in the journey map. Journey stages vary depending on the scenario, so companies often use data to help them determine the content of the stage.
Behavior: The actual actions and steps taken by the user
Thoughts: The user's thoughts, problems, motivations, and information needs during different stages
Emotion: Usually a single line is used to represent the ups and downs of emotions during the user experience.
Gains and insights: Insights gained from the journey map provide methods for optimizing the user experience. Gains can help products gain information from the journey map: With this information, what do we need to do? Who has what changes? Where are the biggest opportunities? How should we measure the improvements that have been implemented?
2)Journey map operation steps
Step 1: For a certain type of product or service, collect a series of user goals, scenarios and behaviors, and classify the stages on the timeline.
Step 2: Add the user’s thoughts and emotions to further enrich the content on the timeline and make the whole process more narrative. Step 3: Condense the narrative of the process into a visual diagram to convey insights and provide information for the product design process.
3)User Journey Map Template
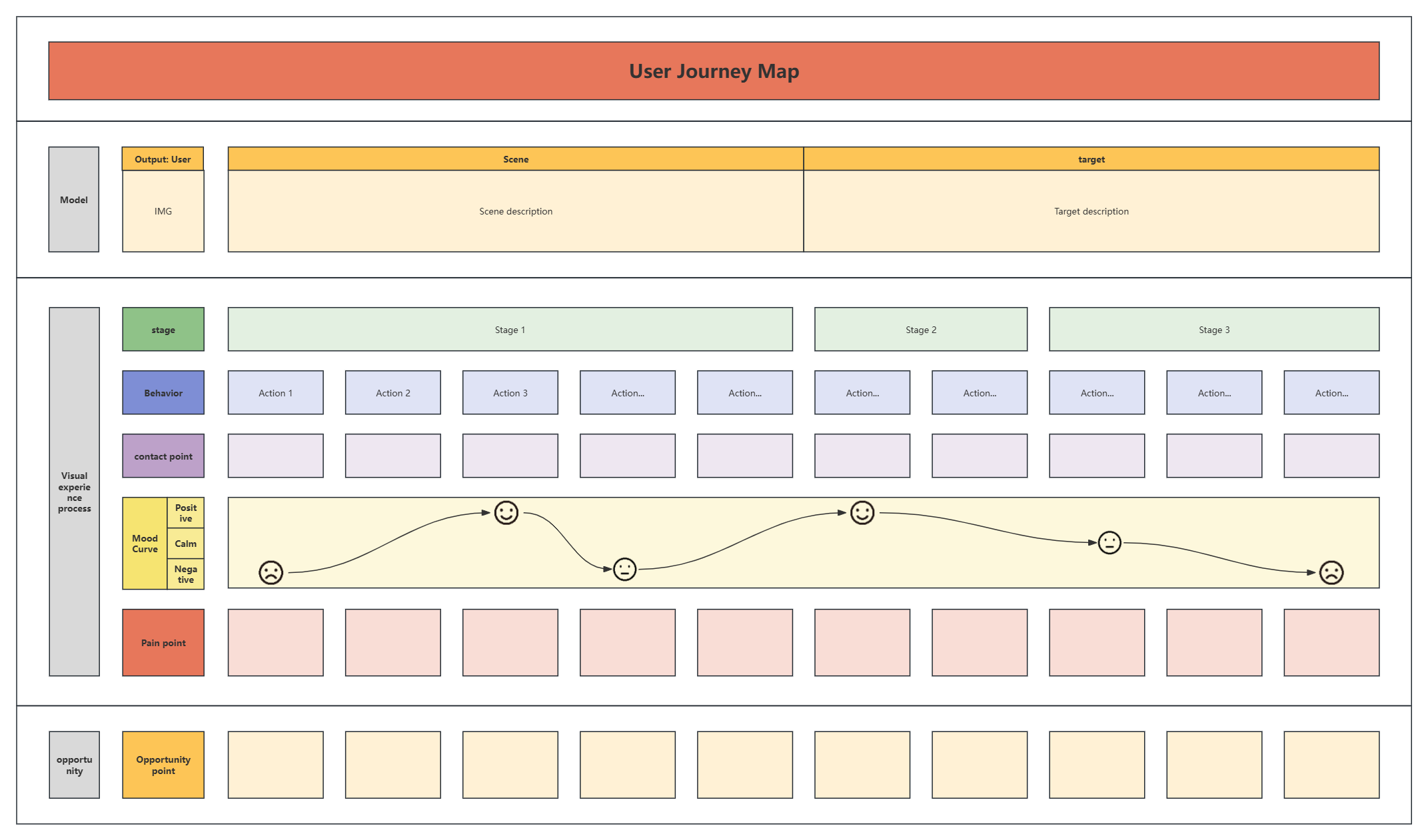
User Journey Map Template-Color Style
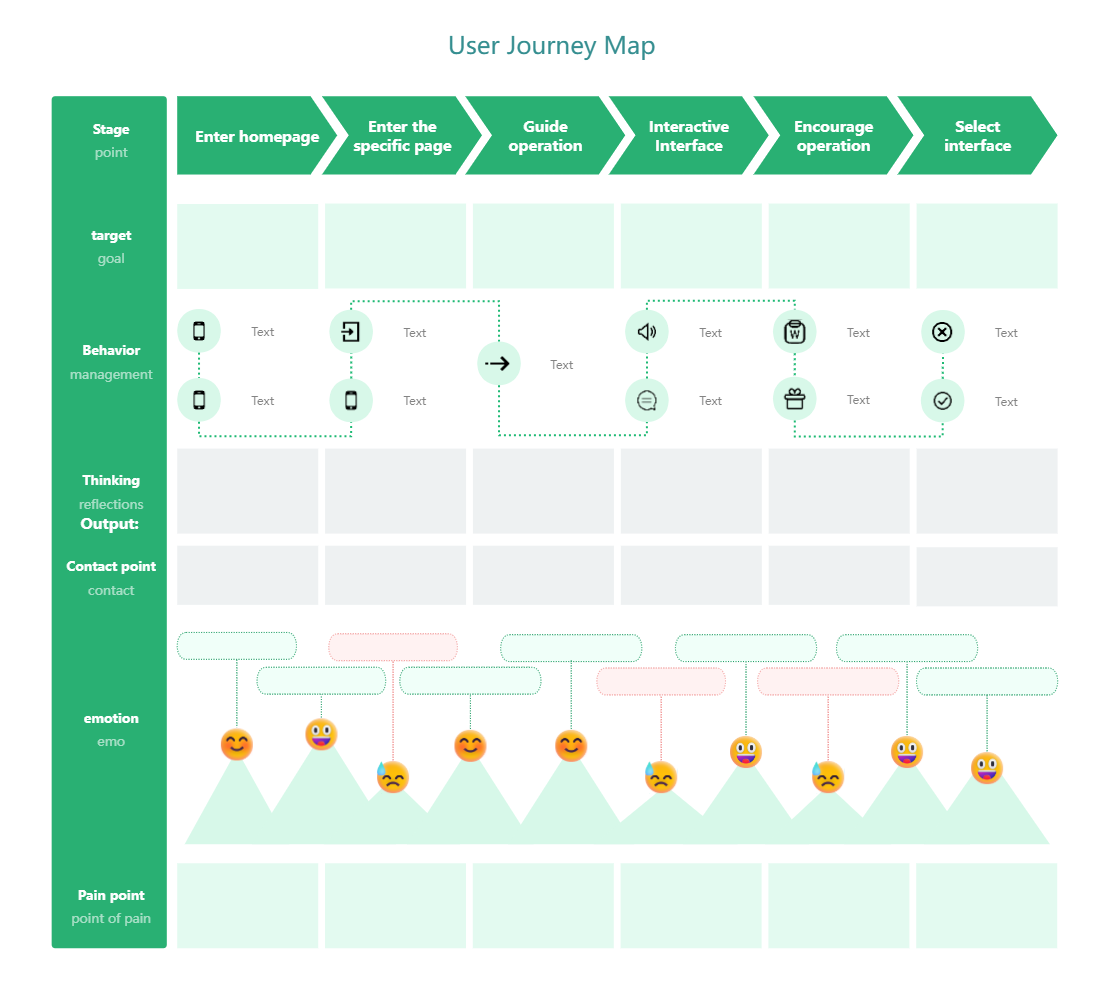
User Journey Map Template-Green Style
4. Service Blueprint
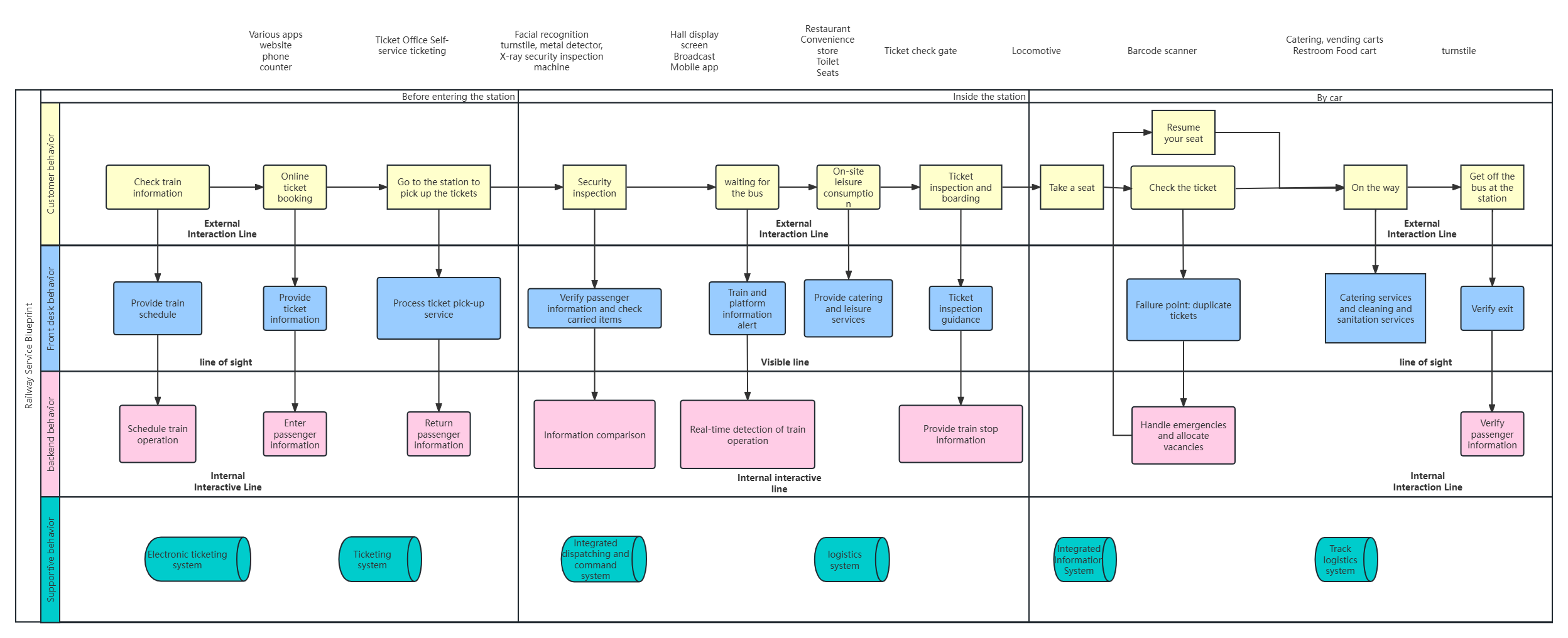
1)What is a service blueprint?
It can be understood as an extension of the user journey map. The service blueprint more comprehensively displays the front-end and back-end collaborative process system that supports user experience. It focuses on the overall collaborative process within the enterprise. From the perspective of the enterprise, based on the customer journey, how the enterprise provides support and interaction in all directions, multiple touchpoints, and across functions or departments.
2) Key elements of the service blueprint
Physical display: the points of contact between users and products/services
Customer behavior: the behavior of users in the process of using products/services
Front-end behavior: the service operations that users can see in the process of using products
Back-end service: the behavior of back-end employees in the process of users using products
Support process: the process of internal interaction between employees flowing between systems
3) Service blueprint operation steps
Step 1: Find support. Establish a core interdisciplinary team and build stakeholder support.
Step 2: Define goals. Define the scope and align with the goals of the blueprint plan.
Step 3: Collect research. Use a variety of methods to gather research from customers, employees, and stakeholders.
Step 4: Draw a blueprint. Use this research to fill out a low-fidelity blueprint.
Step 5: Refine and distribute. Add additional content to refine the high-fidelity blueprint that can be distributed among clients and stakeholders.
This is what we are going to share today about how to evaluate and analyze user experience during the product life cycle . User experience is the key to product success, and it is directly related to user satisfaction and loyalty. Therefore, we need to improve product experience by continuously optimizing design, improving interaction fluency, and paying attention to user feedback .