Today I will introduce to you a continuous improvement tool - the PDCA Deming Cycle Model. PDCA is the four stages of quality management. It is currently applied to many fields. It can help you manage projects and even manage your life, allowing you to keep your eyes on the goal, work hard to execute, while constantly checking, optimizing and correcting until you succeed.
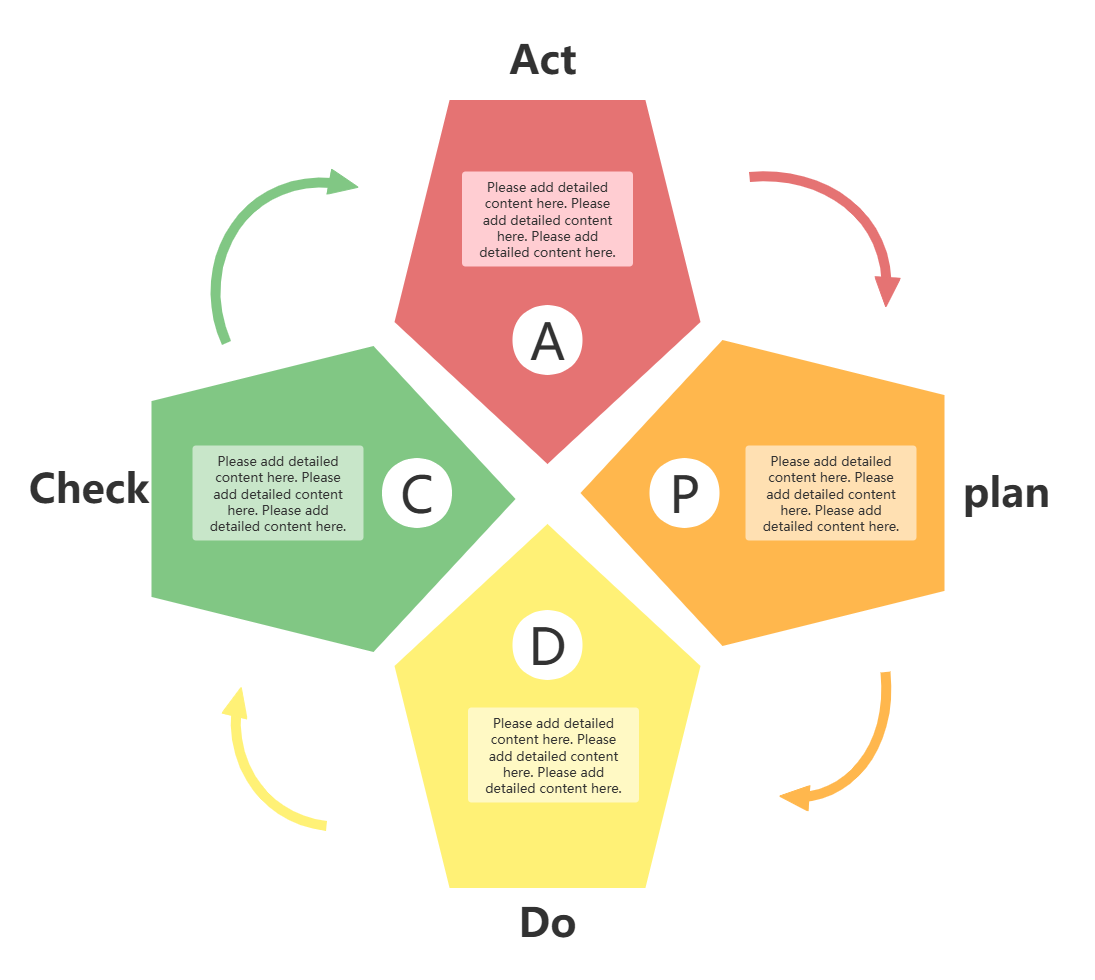
The PDCA cycle method was first proposed by Walter A. Shewhart, an American quality management expert. It was adopted and promoted by Deming and became popular, so it is also called the Deming cycle. The meaning of the PDCA cycle method is to divide management into four stages : Plan, Do, Check, and Act. In management activities, it is required to make plans, implement plans, check the implementation effects, and then include successful ones in the standards, and leave unsuccessful ones to the next cycle. This working method is the basic management method and the general rule of various management tasks of enterprises.
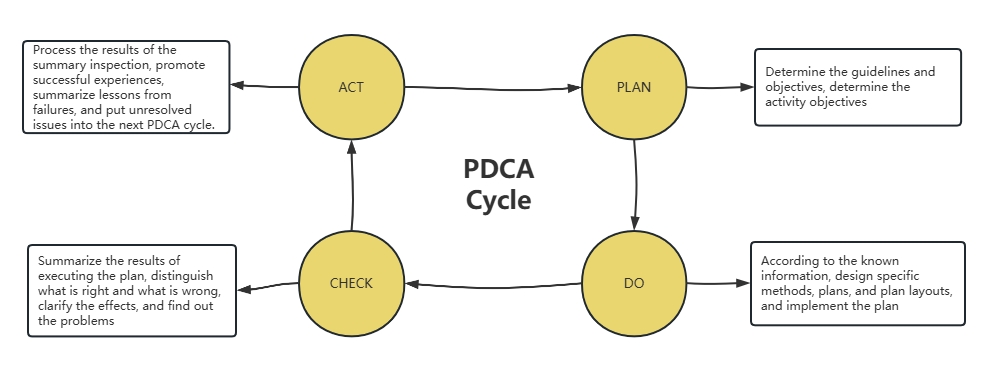
P (Plan): Plan. Determine the policy and objectives, and determine the activity plan;
D (Do): Execute. Do it on the spot and realize the contents of the plan;
C (Check): Check. Summarize the results of the execution of the plan, pay attention to the effects, and find out the problems;
A (Action): Action. Process the results of the summary and inspection, affirm the successful experience and appropriately promote and standardize it; summarize the lessons of failure to avoid recurrence, and put unresolved problems into the next PDCA cycle.
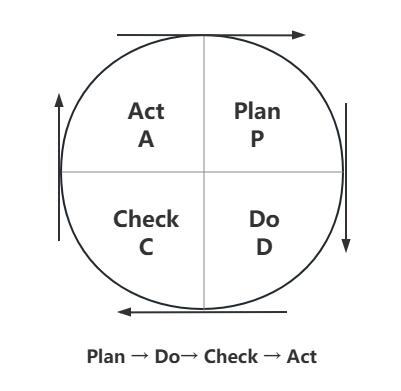
1. Repeating the Same
The four processes of the PDCA cycle are not completed after one run, but are repeated over and over again. After a cycle is completed, some problems are solved, but there may still be problems that have not been solved, or new problems have arisen, and the next PDCA cycle will be carried out, and so on.
2. Big ring inside small ring, small environmental protection big ring
Similar to a planetary gear system, the relationship between a company or organization's overall operating system and its internal subsystems is an organic logical combination of large rings with small rings.
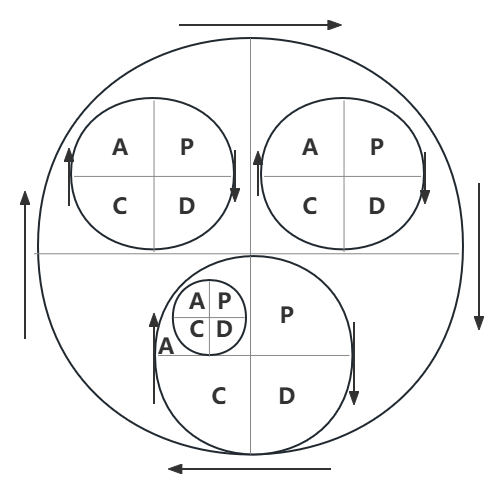
Schematic diagram of PDCA big ring inside small ring
3. Step-by-step rise
The PDCA cycle is not a cycle that stays at one level. The process of continuously solving problems is a process of gradually rising levels. The quality improves with each cycle.
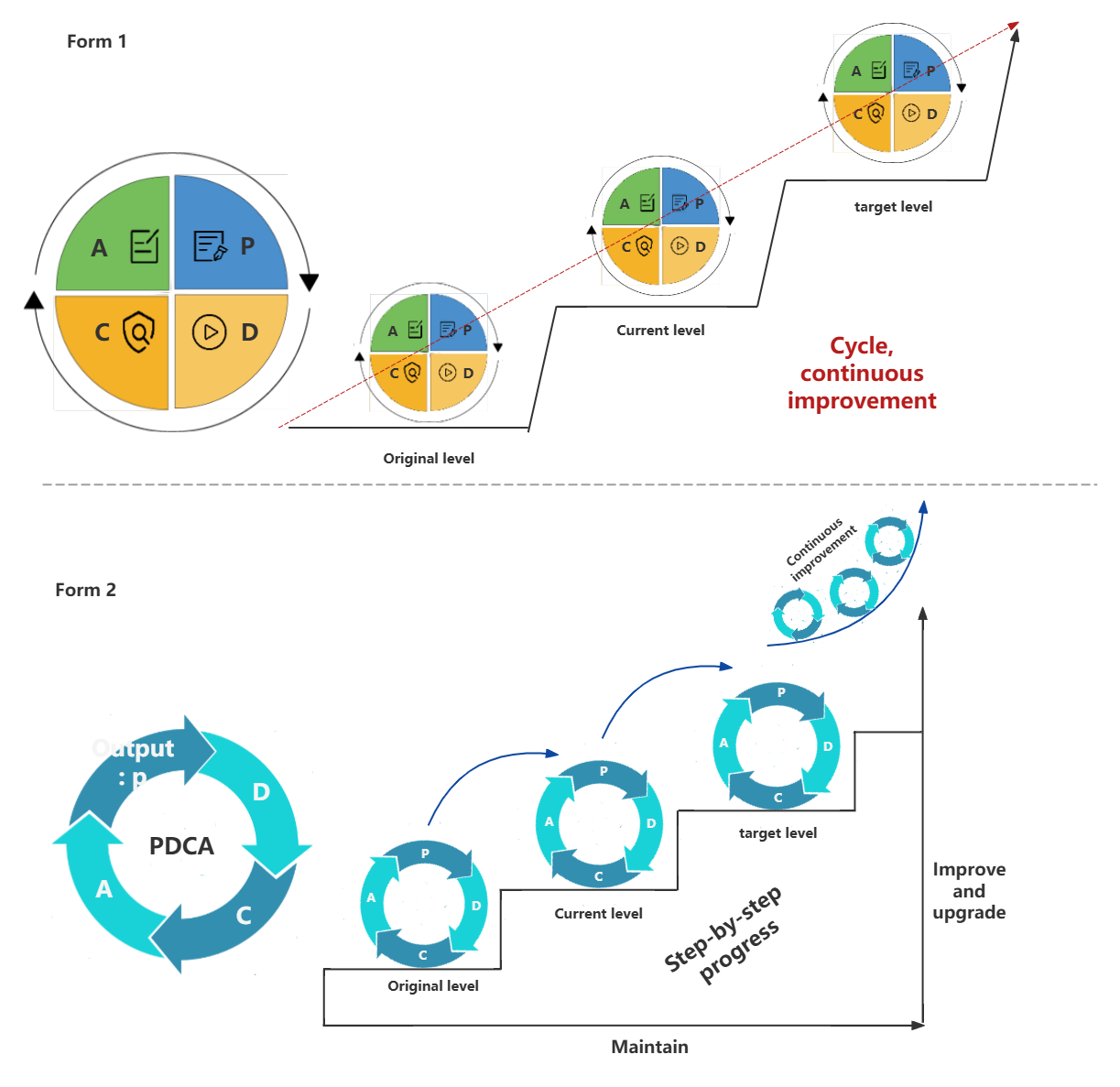
4. Statistical tools
The PDCA cycle applies scientific statistical concepts and processing methods as an effective tool for promoting work, discovering problems and solving problems. The typical model is called "four stages" and "eight steps". Next, I will explain the PDCA "four stages" and "eight steps" in detail.
1. The four stages of PDCA
1) Planning stage
Through market research, user visits, etc., we can find out the user's requirements for product quality, determine the quality policy, quality objectives and quality plan, etc. This includes current situation investigation, analysis, determination of factors and formulation of plans.
2) Design and Implementation Phase
Implement the contents stipulated in the previous stage. Carry out product design, trial production, testing and personnel training before plan execution according to quality standards.
3) Inspection phase
During or after the execution of the plan, check the implementation status to see whether it meets the expected results of the plan.
4) Processing stage
According to the inspection results, take corresponding measures to consolidate the achievements, incorporate successful experiences into the standards as much as possible, and standardize them. The remaining problems will be transferred to the next PDCA cycle to be solved, that is, to consolidate the measures and the next step.
2. The eight steps of PDCA
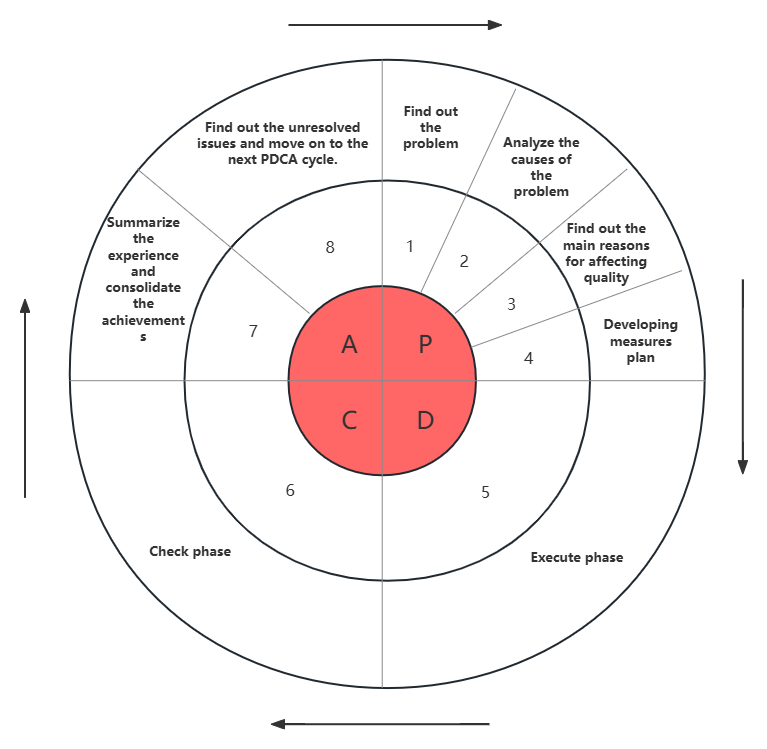
Step 1: Find out the existing problems. Before making a plan, analyze the current situation and find the problems, just like a doctor examining a patient.
Step 2: Analyze the cause of the problem. There are many analysis methods, and the fishbone diagram, 5W+2H, 4M and other methods are recommended .
Step 3: Find the main cause. After analyzing all the causes, focus on finding the main cause. Only by solving the main cause can the root problem be solved.
Step 4: Develop a plan of action. The next step is to develop a plan of action for the next step, mainly considering how to develop measures, what the goal is, where to start, who is responsible, when to start, and how to do it.
Step 5: Execution phase. Just follow the plan.
Step 6: Check phase: Compare the execution results with the goals.
Step 7: Summarize experience. Summarize successful experience and formulate corresponding standards to improve future work efficiency.
Step 8: Find unresolved problems and move on to the next cycle. One cycle may not solve all problems. If one cycle cannot solve the problem, move on to the next cycle to continue solving it.
PDCA is generally applicable to most work processes, including project management, manufacturing, recruitment, marketing activities, design applications, media placement, etc. Using PDCA can greatly improve the processes in various corporate tasks, help individuals achieve a closed loop, review and summarize to help growth, improve work efficiency, and avoid ineffective work.
1. PDCA cycle of recruitment in a certain company
P: Analyze the qualifications and job responsibilities of the personnel for the required position, and prepare interview questions and steps.
D: Interview venue layout and interview arrangements.
C: Achievement of total cost-effectiveness of recruitment system
A: Summarize and analyze the scientific nature and success rate of interview questions, the correctness of recruitment channels and interview methods.
2. The PDCA cycle of a company’s layoff plan
P: Evaluate existing positions and formulate a plan to reduce positions and staff.
D: Assign tasks to department heads and execute them within a time limit
C: HR tracks and supervises the reduction plan
A: Improvements such as simplifying work procedures for departments with reduced staff
3. Someone’s PDCA cycle in daily work
P: Today's plan - a list of things to do every day.
D: Full record of today’s affairs, quantified goals, and completion status.
C: Check problems found during work and situations that require attention during work.
A: Reflect on your own studies, work, thoughts, and behaviors, and grow through reviewing them.
The PDCA cycle can be used in daily work and life. It has an advantage. For example, if your goal is to reduce a certain indicator by 50%, even if the result cannot meet the expectation, it will be reduced by 40% or 30%. As long as you do it, it will be effective. The quality will improve with each cycle.
We have prepared several PDCA cycle templates for your convenience. Just click the link below the picture to use them.
1. Continuous Cycle Deming Circle Diagram
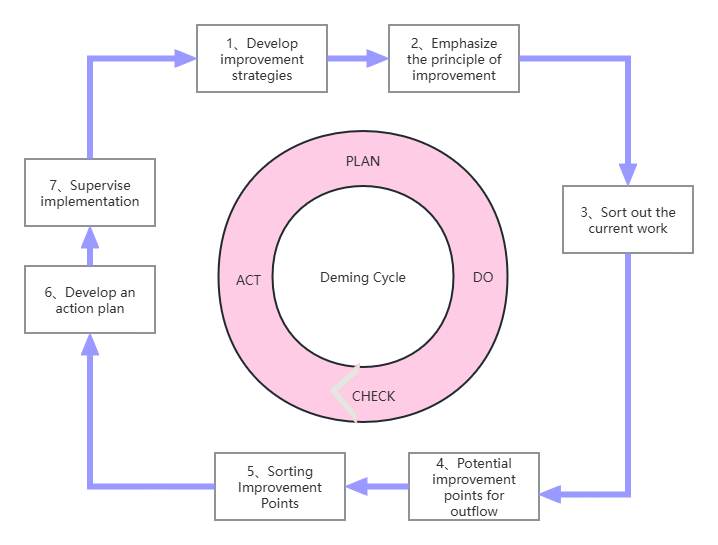
Continuous Improvement-Deming Cycle
2. Use the PDCA cycle to improve care
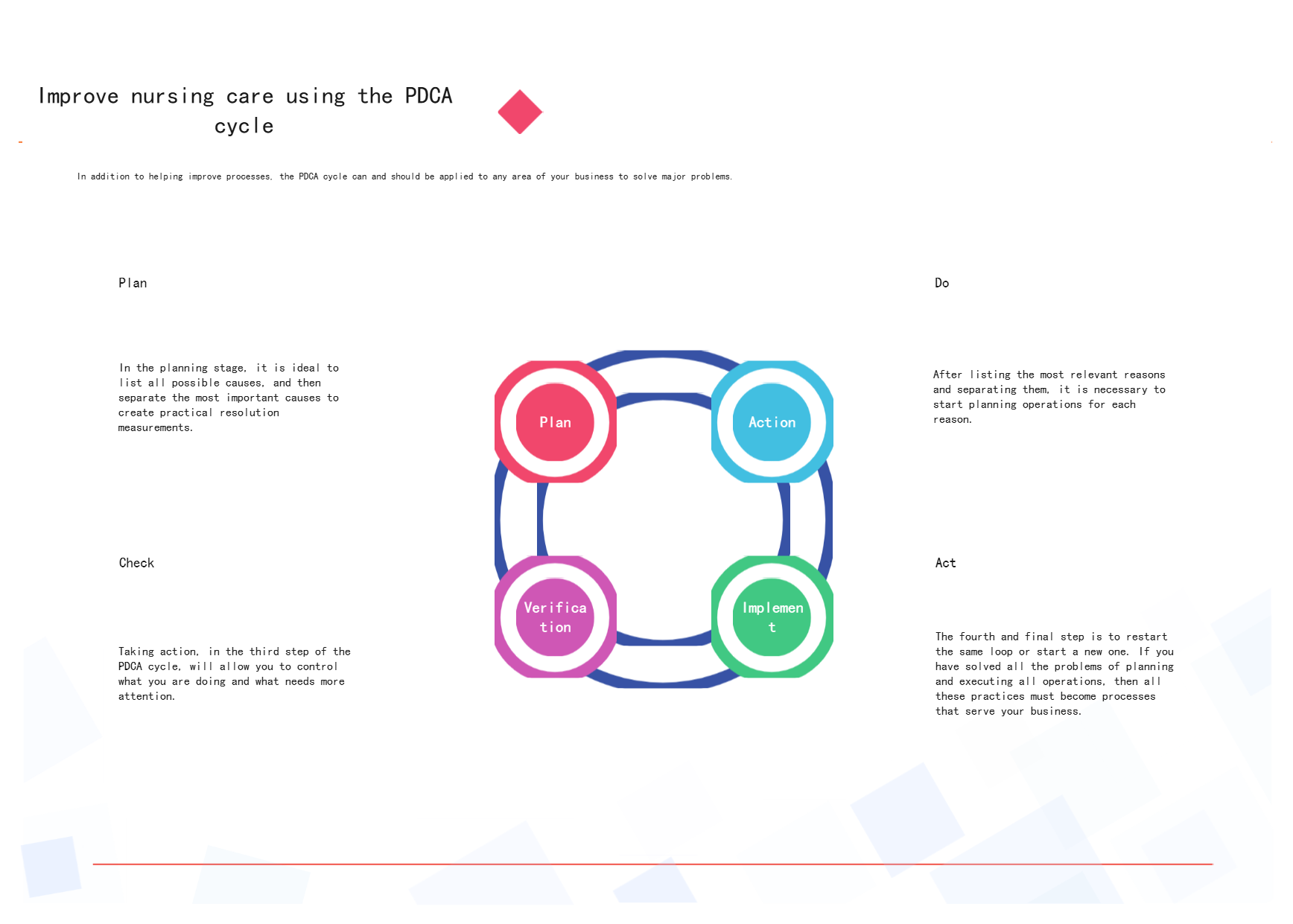
PDCA cycle to improve nursing care
3. International Talent Training Program - PDCA Cycle
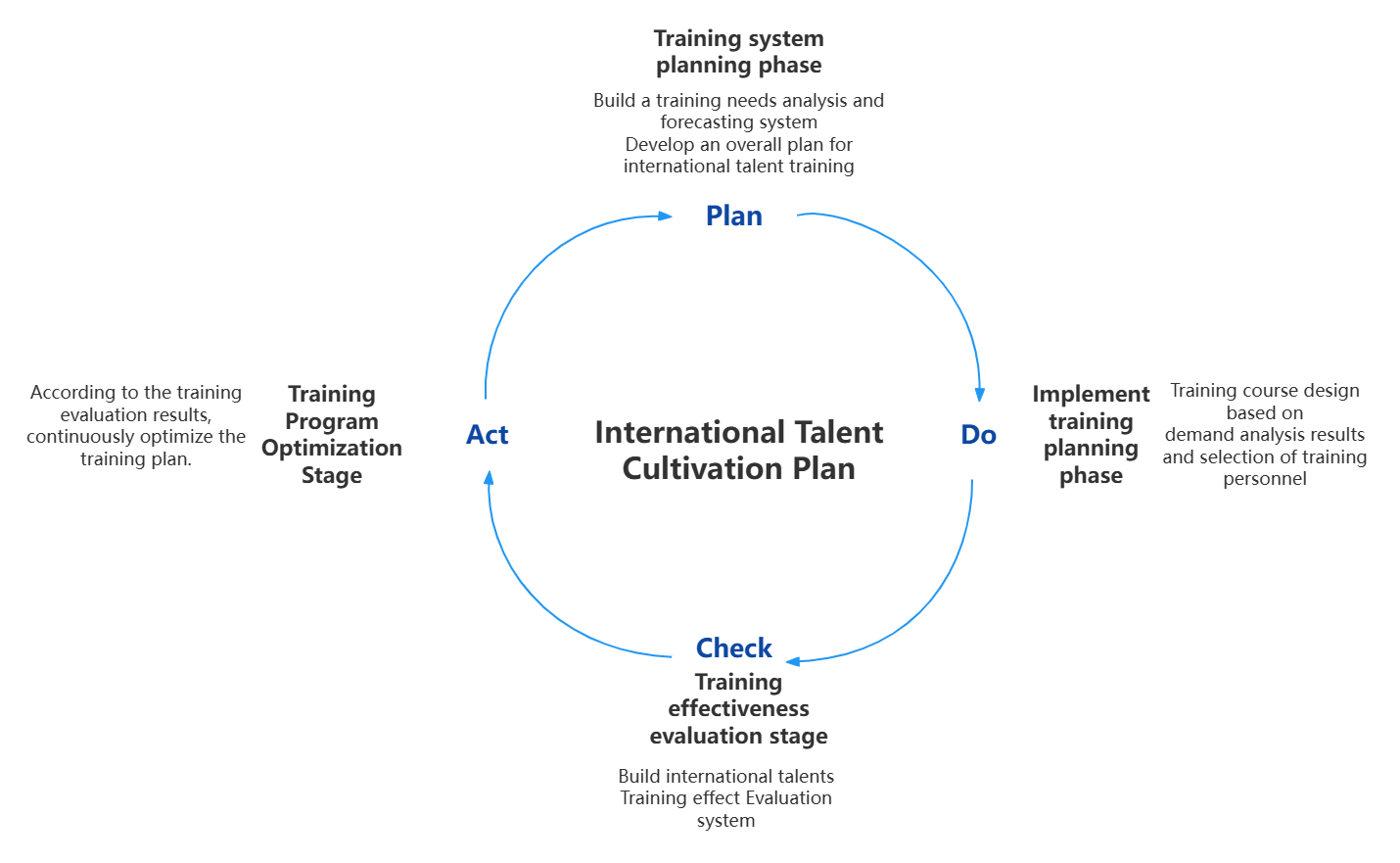
International Talent Training Program-PDCA Cycle
4. PDCA Cycle
PDCA Deming Circle Diagram Template
Every time you turn the PDCA cycle, problems will be reduced, product quality will improve, work will be more efficient, and management levels will become higher and higher. The PDCA cycle is actually a tool for continuous improvement. I hope everyone can make reasonable use of it in daily work and life.