

In today's highly competitive business environment , the human resource management model is undergoing profound changes, among which the three-pillar transformation has become the focus of many companies.
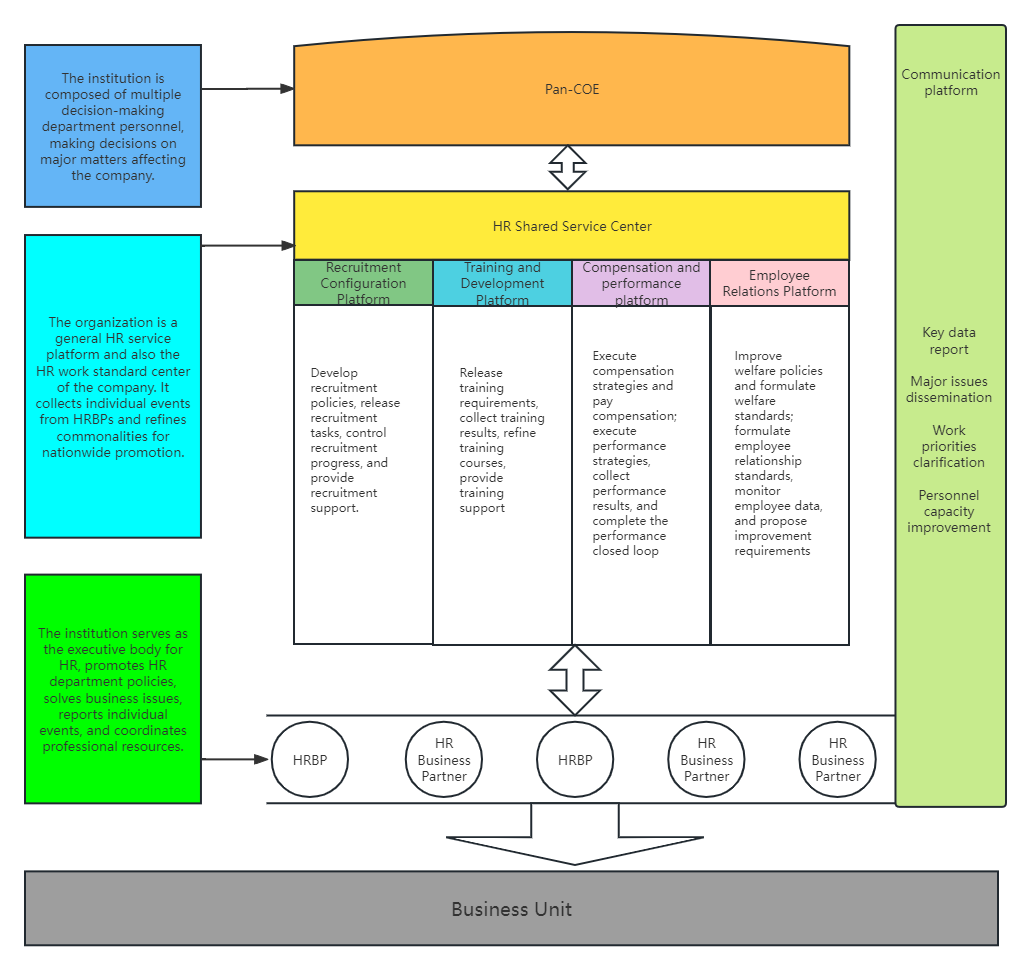
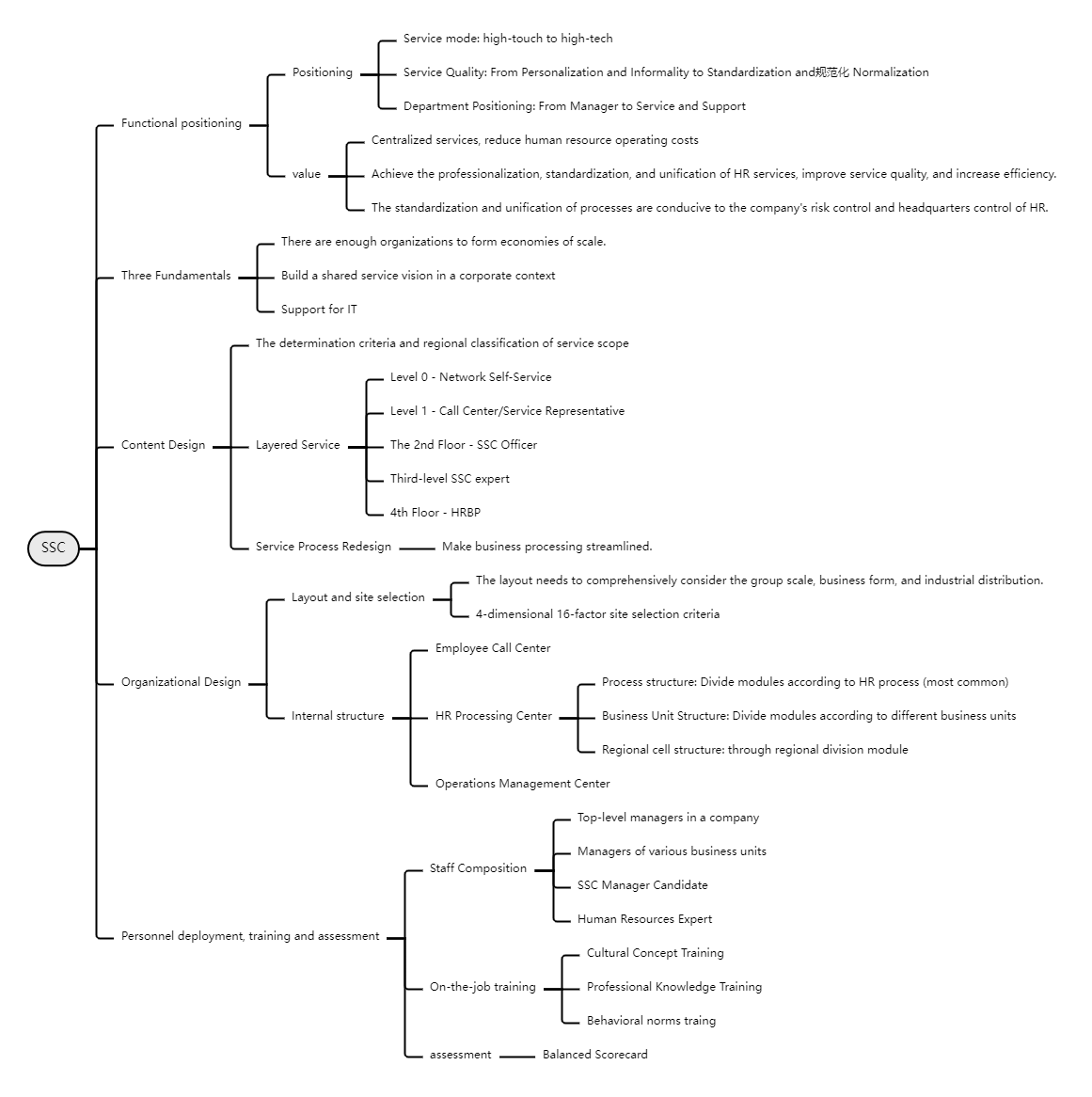
First look at SSC (Shared Service Center) , its functional positioning has undergone significant changes in many aspects. In terms of positioning, service methods have evolved from high-touch to high-tech, service quality has moved from individuality and casualness to standardization and standardization, and department positioning has also changed from managers to service and supporter. In terms of value expression, SSC can centralize services and significantly reduce human resources operating costs; realize professionalization, standardization and unification of HR services, greatly improve service quality and increase efficiency; and the standardization and unification of processes help the company to HR risk management and headquarters management and control.
The successful construction of SSC requires three major foundations: a sufficient number of organizations to form a scale effect, the establishment of a shared service vision that fits the company's background, and the strong support of IT.
At the content design level, the standards and regional grading of the service scope need to be determined. Tiered services include network self-service at level 0, call center/service representative at level 1, SSC specialist at level 2, SSC expert at level 3, and HRBP at level 4. The key to service process redesign is to make business processing more streamlined.
HR Three-Pillar Transformation-SSC
In terms of organizational design, layout and site selection should comprehensively consider the group's scale, business form and industrial distribution, and follow the site selection criteria of 4 dimensions and 16 elements. Its internal structure covers the employee call center and HR process transaction processing center. The process structure of the processing center can be divided into modules according to HR processes, business units or regions, and an operations management center must also be established.
Staffing, training and assessment should not be neglected. The staffing structure includes senior managers, managers of various business units, SSC manager candidates, human resources experts, etc. On-the-job training includes cultural concept training, professional knowledge training and behavioral norms training. Assessment can adopt the balanced scorecard method.
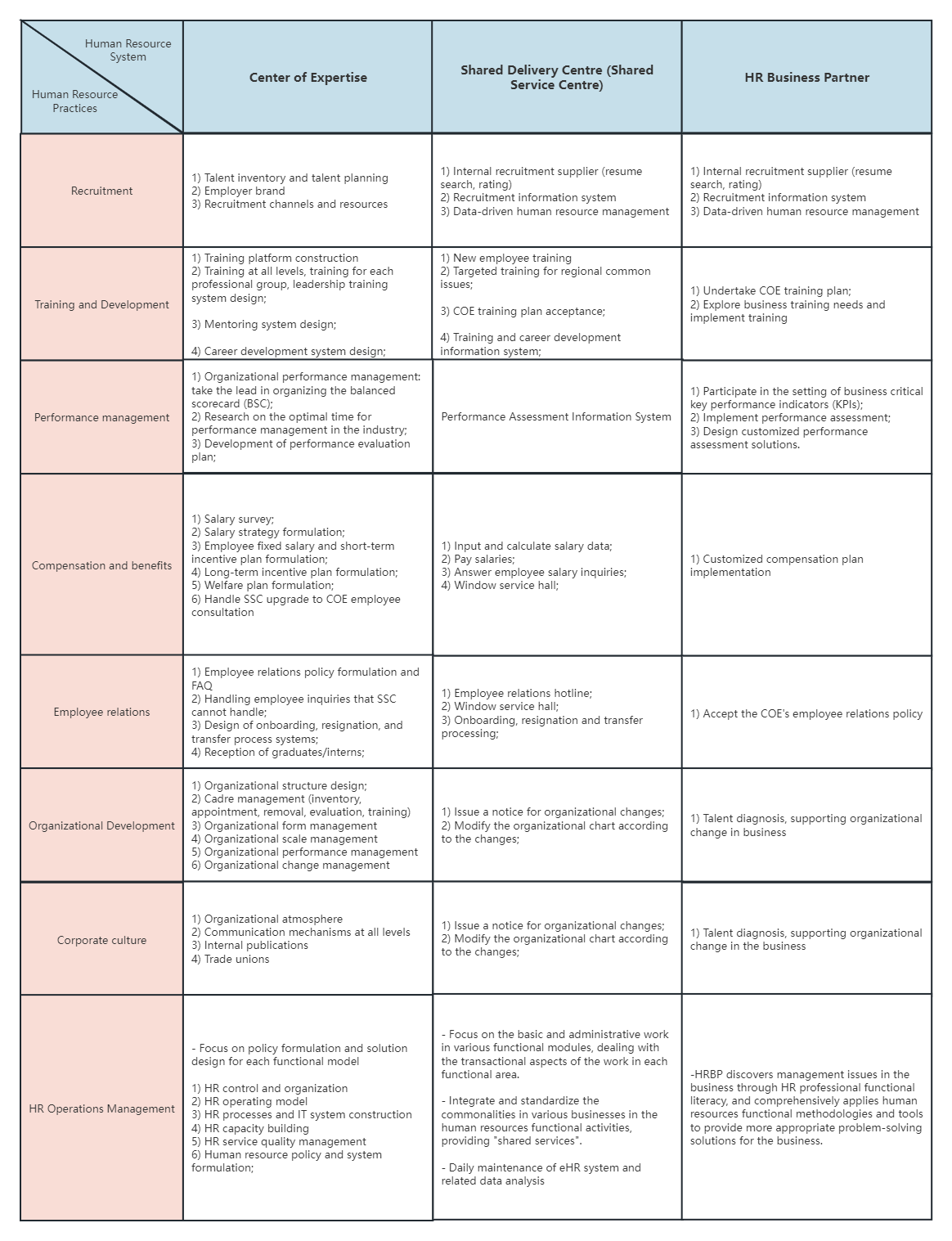
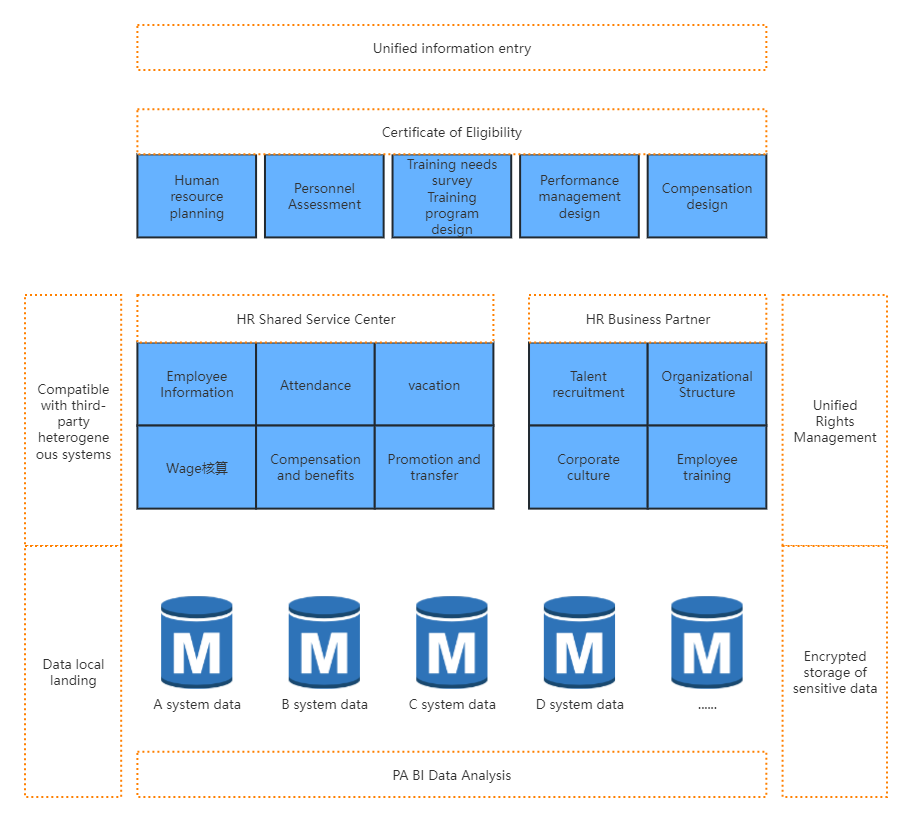
The relationship between the three pillars of HR and functional modules
Next up HRBP (Human Resources Business Partner) . Its role is clearly defined and involves three types of HR work, namely transactional work, tactical work and strategic work. The roles include strategic partner, HR calendar manager, change promoter and relationship manager. Key activities include helping to achieve performance goals, building the soft power of the business team and understanding the individual needs of employees. HRBP has undergone a series of changes, such as from module management to overall intervention, from providing services to providing consulting, from independent management to mutual penetration, and from focusing on HR output to focusing on business performance. HRBP is divided into business type and cultural type.
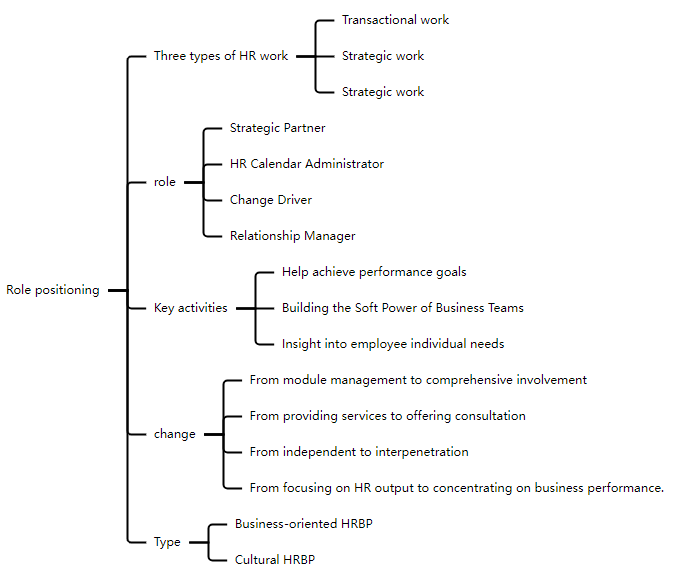
HR Three Pillars Transformation-HRBP
The realization of the role requires three steps: clarify the business needs faced by HRBP, including performance, behavior, work environment and ability requirements, and understand the business by visiting the business department; convert it into executable HR solutions, such as using IBM's business leadership model, organizational capability "Yang Triangle", fishbone diagram, GAPS and other methods; then communicate, trust and win support through the implementation of strategic cooperation projects, identify real customers, find key people, and establish reliability and trust. Key elements include knowledge requirements and core capabilities. Knowledge requirements include business knowledge and professional knowledge. Core capabilities include professional capabilities, business sensitivity, consulting and diagnostic capabilities, and interpersonal connections. In terms of configuration and reporting relationships, the architecture is divided into business-oriented and functional HRBPs based on the service objects, and the levels are set as junior/supervisory level, intermediate/manager level and senior/director level. Reporting methods include dispatched or "HR representative type", reporting directly to the head of the human resources department, and affiliated or "division type", reporting directly to the head of the business department. Training practices include regular training of business knowledge and HR knowledge, job rotation, project participation and regular sharing and communication. Assessment is carried out through result indicators, key task indicators and customer indicators.
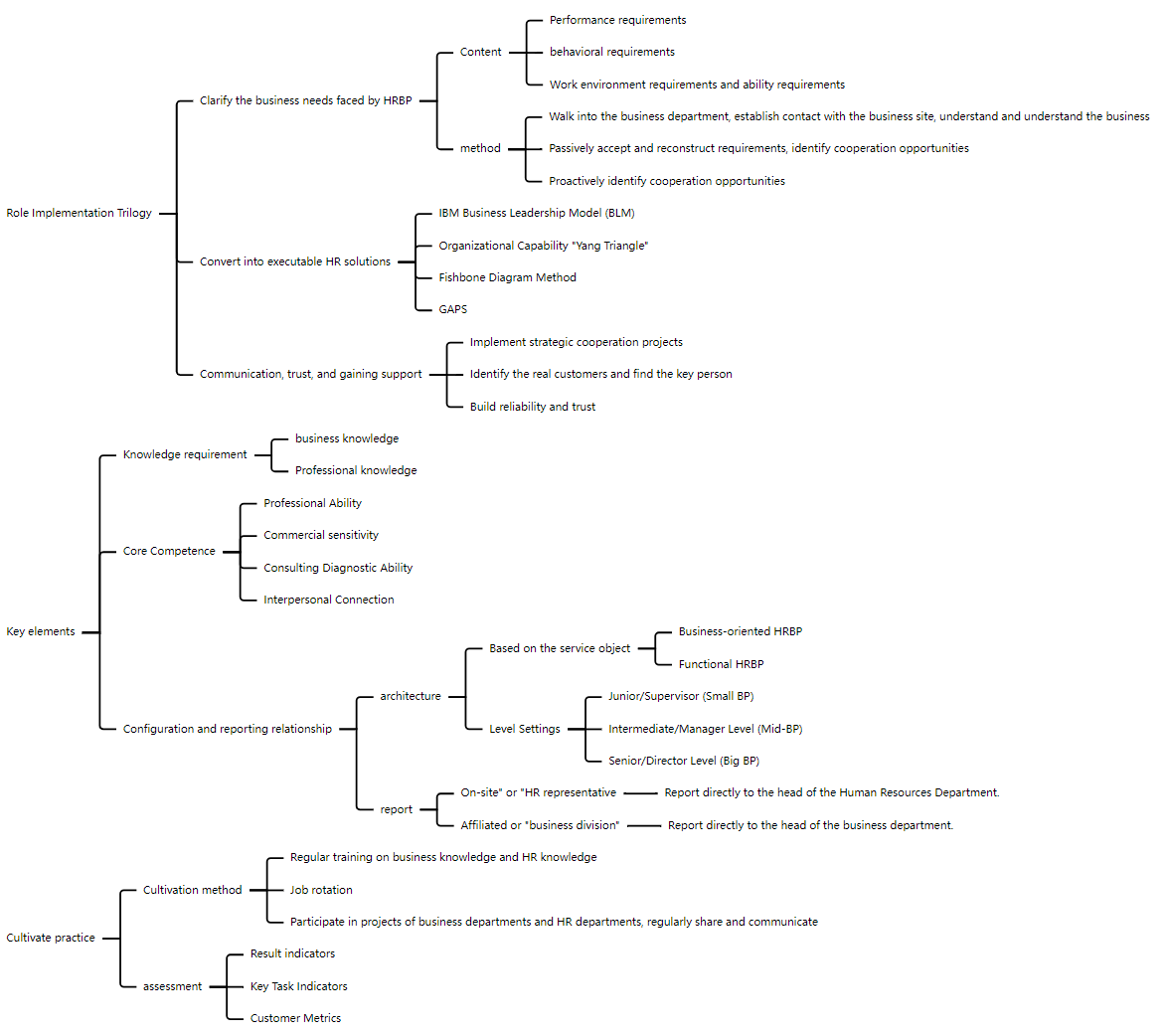
HR Three Pillars Transformation-HRBP
Looking at the COE (Center of Experts) , its roles include designer, technical expert, controller and knowledge transmitter. To give full play to the role of experts, it is necessary to clarify the role requirements and match people with roles, align with business challenges, focus on solution delivery, identify initiators and possible participants, maintain close contact with BP and SSC, and strengthen communication with other departments of the company. Capability requirements cover professional core capabilities and consulting capabilities. The improvement plan includes customized plans, communication with training leaders, performance management, training, and improving capabilities at work. At the same time, it is configured and assessed through procedural indicators and operational indicators.
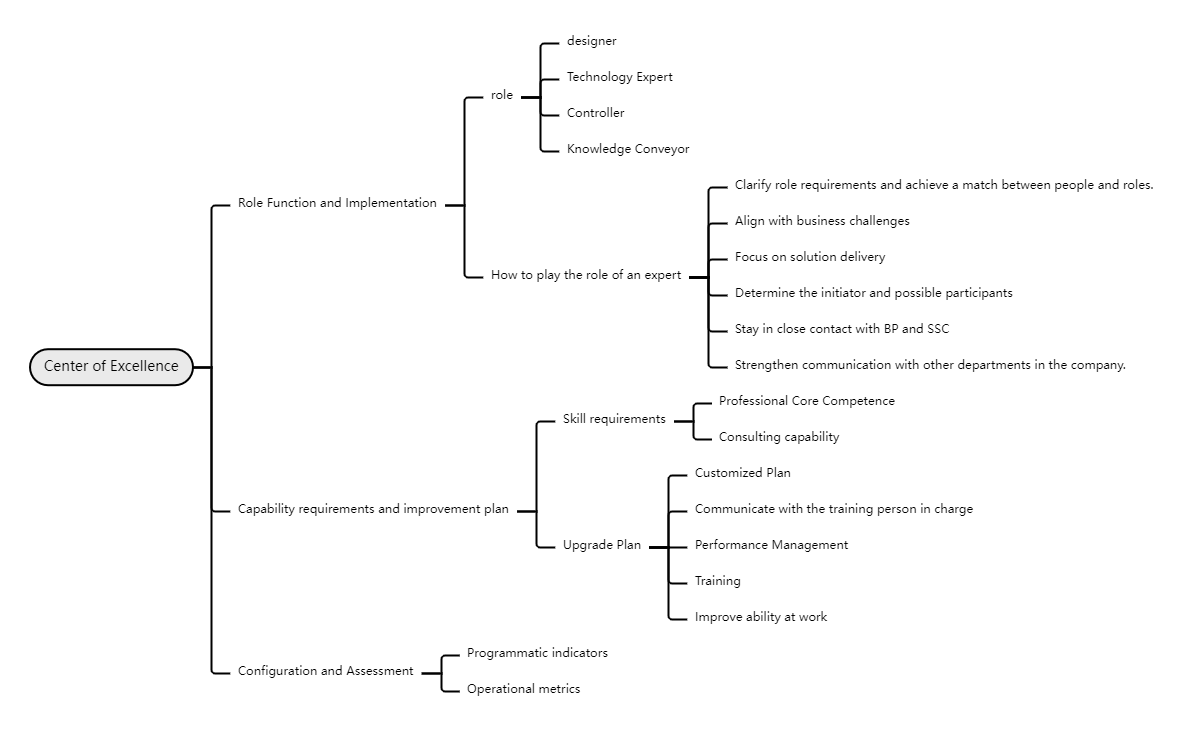
HR Three-Pillar Transformation-COE
In terms of change, the existing division of labor has certain problems, such as HRM being out of touch with on-site business needs, high personnel costs, and not conducive to human resource management and control. The three pillars have clear division of labor, with HRBP providing human resource support according to the division of labor of business units, HRSSC providing service platforms according to regional division of labor, and HRCOE exerting professional talents according to functional module division of labor. Its value lies in realizing the transformation of HRM from professional orientation to business orientation, and from transactional HR to strategic HR, but it also faces many challenges, such as balancing the relationship between company control goals and individual needs, unclear role positioning and ability defects of HRBP, and effective division of labor and cooperation among the three pillars.
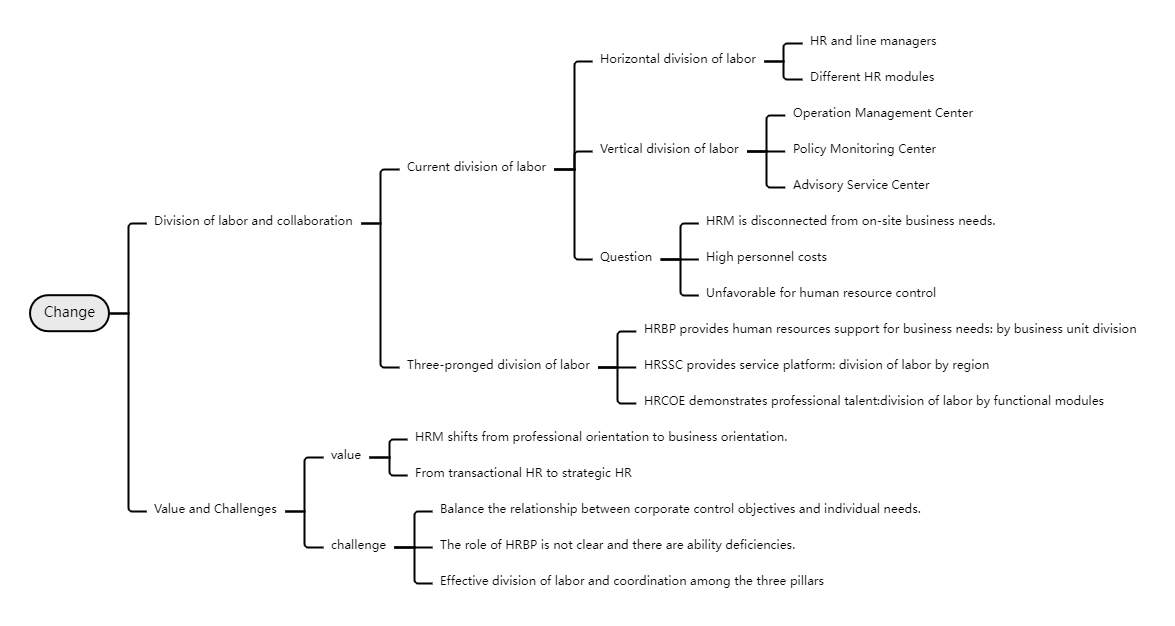
HR three-pillar transformation
Finally, ProcessOn's free online mind map can intuitively show the relationship and hierarchy of each branch in the three pillars of human resources. For example, when describing the three pillars (HRBP, HRSSC, COE), you can expand the details of each pillar, such as the role positioning, key activities, training practices, etc. of HRBP; the functional positioning, three foundations, content design, etc. of HRSSC; the role functions and implementation, capability requirements and improvement plans of COE, etc.
Through ProcessOn mind mapping, we can quickly sort out the complex information and logical relationships in the three pillars of human resources, helping people to understand this concept more comprehensively and deeply. At the same time, the visualization characteristics of mind mapping make the structure and key points of the three pillars clear at a glance, which is helpful for memory and review.
In short, ProcessOn mind map is an effective tool for presenting and analyzing the three pillars of human resources, which can help people master relevant knowledge and key points more efficiently.